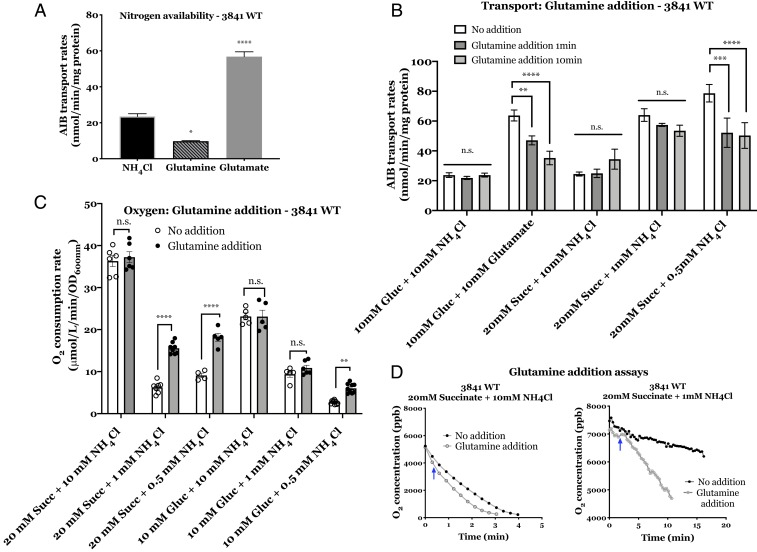
Fig. 5.
Effect of glutamine on the PTS regulatory cascade of Rlv3841. (A) Effect of nitrogen availability on AIB transport. Membrane transport of wild-type cells grown on UMS with 10 mM glucose as carbon source and 10 mM NH4Cl, glutamine (N-rich conditions) or glutamate (N-limiting conditions). (B) Effect of glutamine addition on AIB transport. Wild-type cells grown on UMS with 10 mM glucose as carbon source and 10 mM NH4Cl (N-rich conditions) or 10 mM glutamate (N-limiting conditions). Transport rates measured at 1 min and 10 min after glutamine addition. All transport rates are expressed in nmol min−1 mg protein−1. (C) Effect of glutamine addition on O2 consumption of cells grown under different nitrogen conditions. Wild-type cells grown on UMS with 20 mM succinate as carbon source and 10 mM NH4Cl (N-rich conditions) or 1 mM NH4Cl (N-limiting conditions). Values show the rates of O2 consumption expressed in μmol L−1 min−1 OD600nm-1. (D) Effect of glutamine addition on O2 concentration over time. Graphical representation of O2 concentration (ppb) over time (min) for cells with no glutamine added (Top line, filled dots) compared to cells after the addition of glutamine (100 μM) indicated by a blue arrow (Bottom line, empty dots). Conditions are as above. Data are averages (±SEM, at least three independent cultures). Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (*) P < 0.05, (**) P < 0.01, (***) P < 0.001 (****), P < 0.0001 and n.s. not significant.