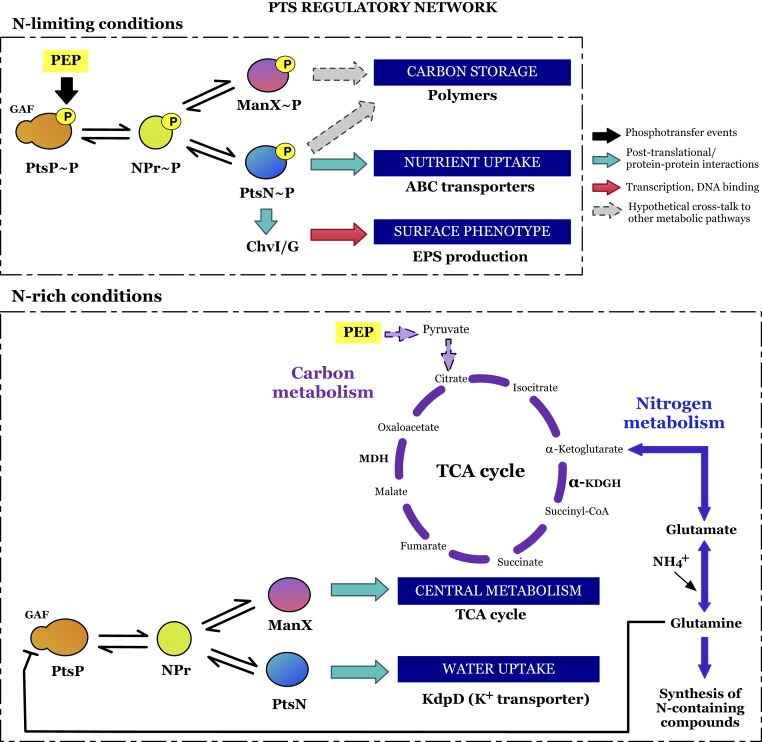
Fig. 8.
Schematic model for PTS interactions according to nitrogen availability. Under N-limiting conditions, PtsP autophosphorylation via PEP modulates the phosphorylation of NPr and subsequentially, PtsN (EIIANtr) and ManX (carbohydrate-EIIA). Once phosphorylated, PtsN activates ABC transporters and interacts with ChvI to control EPS production, with both phosphorylated EIIAs possibly acting on carbon storage. Under N-rich conditions, intracellular glutamine inhibits PtsP autophosphorylation and, therefore, the upcoming phosphorylation of PTS components. Dephosphorylated PtsN interacts with KdpD, controlling K+ homeostasis, and ManX acts on the TCA cycle. Dual control of PtsN and ManX mediated by the NPr switch is affected by nitrogen availability, balancing carbon metabolism.