Fig. 3.
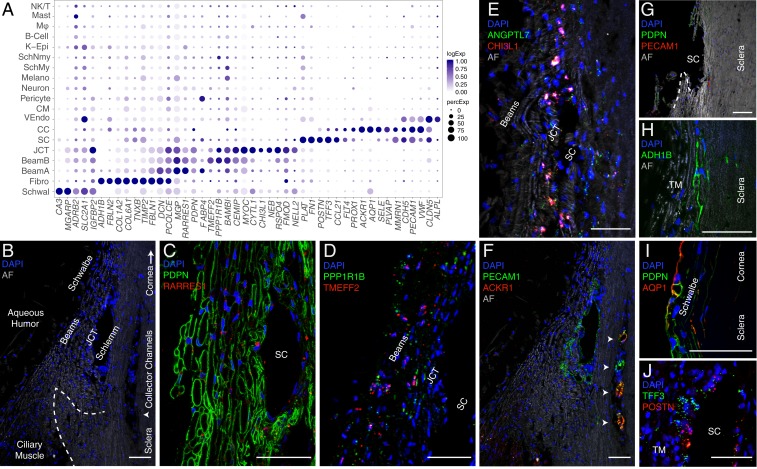
Cells of the human conventional outflow pathway. (A) Dot plot showing genes selectively expressed in cells of the conventional outflow pathway. In this and subsequent figures, the size of each circle is proportional to the percentage of cells expressing the gene, and the shade intensity depicts the average normalized transcript count in expressing cells. Fibro, fibroblast; K-Epi, corneal epithelium; Melano, melanocyte; MØ, macrophage; SchMy, myelinating Schwann cell; SchNmy, nonmyelinating Schwann cell; Schwal, Schwalbe line; VEndo, vascular endothelium. (B) Labeled meridional section of a human corneoscleral rim visualized using autofluorescence (AF) demonstrates outflow anatomy at the iridocorneal angle visualized after removal of iris and ciliary body. The dashed line indicates scleral spur and arrowhead indicates region of CCs. (C) TM (beam and JCT) cells immunostained for PDPN (green) and RARRES1 (red). (D) Fluorescent RNA in situ hybridization against TMEFF2 (red) and PPPR1B1 (green) highlights beam cells. (E) Fluorescent RNA in situ hybridization against ANGPTL7 (green) and CHI3L1 (red) highlights cells in the JCT. (F) Immunostaining for PECAM1/CD31 (green) highlights SC, CCs (arrowheads), and CM capillaries, while ACKR1/DARC (red) costains only the CCs. The same field as in B. (G) Corneoscleral rim section demonstrates the tissue left behind after TM dissection. Very few cells in this region are positive for PDPN (green) or PECAM1/CD31 (red), indicating successful removal of relevant structures (TM and SC) during dissection protocol. (H) Scleral fibroblasts identified in the corneoscleral rim collection immunostained for ADH1B. (I) Schwalbe line cells at the junction of TM and corneal endothelium costain with PDPN (green) and AQP1 (red). (J) Fluorescent RNA in situ hybridization against POSTN (red) and TFF3 (green) highlights SC endothelium. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (nuclear stain). (Scale bars: 50 µm.)