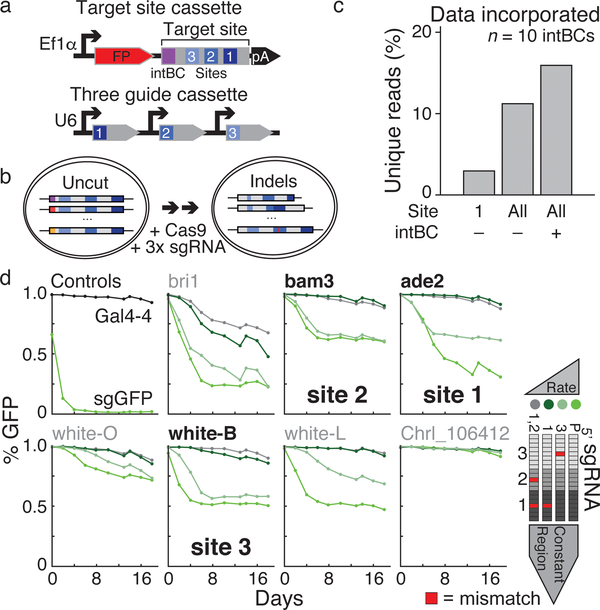
Figure 1: Optimization of a multi-purpose molecular recorder.
a. Target site (top) and three guide (bottom) cassettes. The target site consists of an integration barcode (intBC) and three cut sites for Cas9-based recording. Three different single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) are each controlled by independent promoters (in this study, mU6, hU6, and bU6).
b. Molecular recording principle. Each cell contains multiple genomic, intBC-distinguishable target site integrations. sgRNAs direct Cas9 to cognate cut sites to generate insertion (red) or deletion mutations. Here, Cas9 is either ectopically delivered or induced by doxycycline.
c. Percentage of uniquely marked reads recovered after recording within a K562 line with 10 intBCs for 6 days using the following information: site 1 only with intBCs masked, sites 1–3 (All) with intBCs masked, and sites 1–3 (All) with intBCs considered. Information content scales with number of sites and presence of the intBC.
d. sgRNA mismatches alter mutation rate. Seven protospacers were integrated into the coding sequence of a GFP reporter to infer mutation rate by the fraction of positive cells over a 20 day time course. Single or dual mismatches were made in guides according to proximity to the PAM: region 1 (proximal), region 2, and region 3 (distal). Guides against Gal4–4 and the GFP coding sequence act as negative and positive controls. Bold sequences were incorporated into the target site.