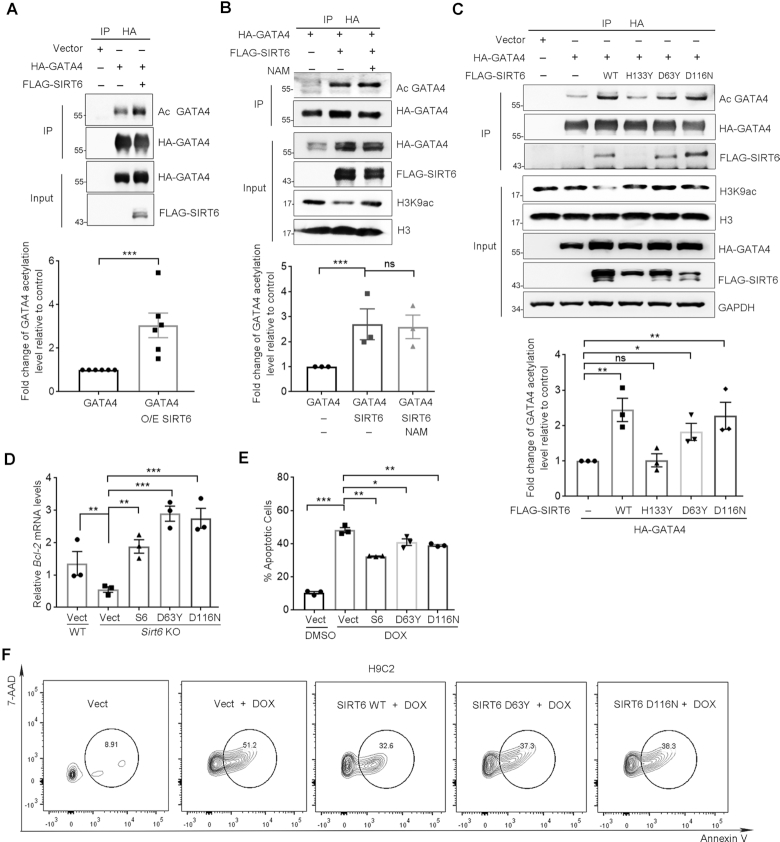
Figure 3.
SIRT6 enhances GATA4 acetylation and protects against DOX-induced myocyte apoptosis independently of its deacylase activity. (A) Western blotting showing the acetylation level of GATA4 immunoprecipitated from HEK293 cells overexpressing of FLAG-SIRT6 and HA-GATA4. Acetylation level was determined with anti-acetyl lysine (AcK) antibodies. Lower, fold change of the acetylation level of GATA4 relative to HA-GATA4 only control, determined by ImageJ. n = 6. ***P < 0.001. (B) HEK293 cells co-expressing FLAG-SIRT6 and HA-GATA4 were treated with 10 μM nicotinamide (NAM) for 4 h. The acetylation level of GATA4 was examined using anti-AcK antibodies following immunoprecipitation. Lower, fold change of the acetylation level of GATA4 relative to HA-GATA4 only control, determined by ImageJ. n = 3. ***P < 0.001. ‘ns’ indicates no significance. (C) HA-GATA4 co-expressed with different forms of FLAG-SIRT6 (WT, D63Y, D116N and H133Y mutant) separately in HEK293 cells was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA beads. The blots of FLAG-SIRT6 in IPs indicate the association of GATA4 and SIRT6. Lower, fold change of the acetylation level of GATA4 relative to HA-GATA4 only control, determined by ImageJ. n = 3. **P < 0.01. *P < 0.05. ‘ns’ indicates no significance. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of mRNA levels of Bcl-2 in WT and Sirt6−/− MEFs re-expressing FLAG-SIRT6, or enzyme-dead mutations. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. 18srRNA was used as a reference gene. (E, F) Representative flow plots and quantification showing the percentages of apoptotic H9C2 cells overexpressing the indicated genes with the treatment of DOX (1 μM, 12 h) following fluorescence-activated cell sorting assay. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.