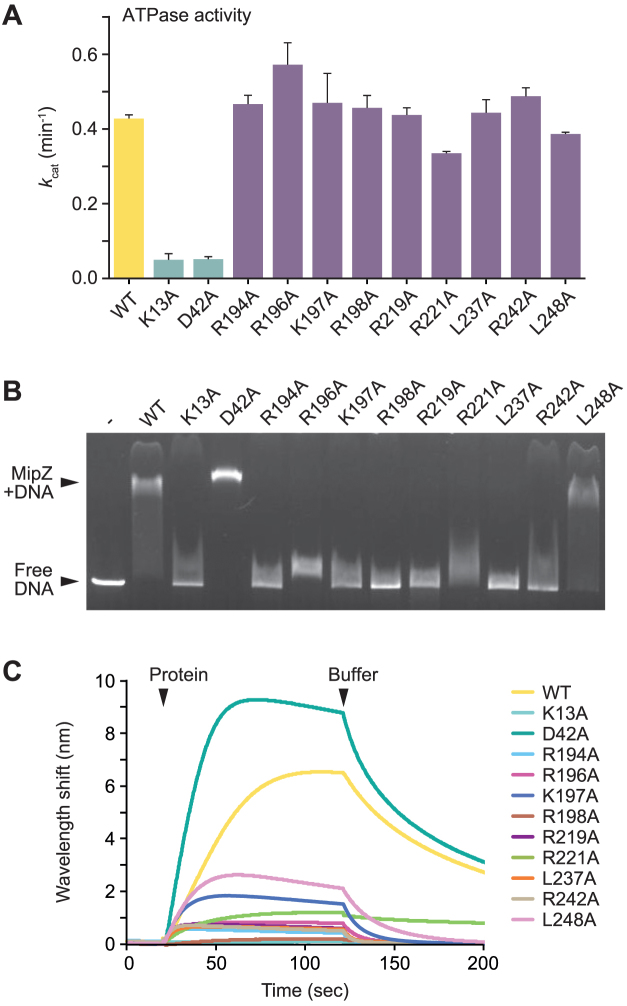
Figure 2.
In vitro characterization of MipZ variants with DNA-binding defects. (A) ATPase activities of purified wild-type MipZ and the indicated mutant derivatives. MipZ (6 μM) was incubated with ATP (1 mM), and the rate of hydrolysis was determined. Shown are the average turnover numbers (kcat) (±SD) from at least three independent experiments. (B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay analyzing the interaction of different MipZ variants with a linearized plasmid (pMCS-2). MipZ (WT) or the indicated variants (10 μM) were incubated with DNA (10 nM) and ATPγS (0.46 mM). Protein-DNA complexes were then separated from free DNA by standard agarose gel electrophoresis. (C) Biolayer interferometric analysis of the DNA-binding activity of different MipZ variants. A biotinylated dsDNA oligonucleotide (rand-biotin/rand-rev; 37.5 μM) was immobilized on the sensor surface and probed with MipZ (WT) or the indicated variants (4 μM) in the presence of ATPγS (1 mM). All analyses were performed at least three times, and representative results are shown.