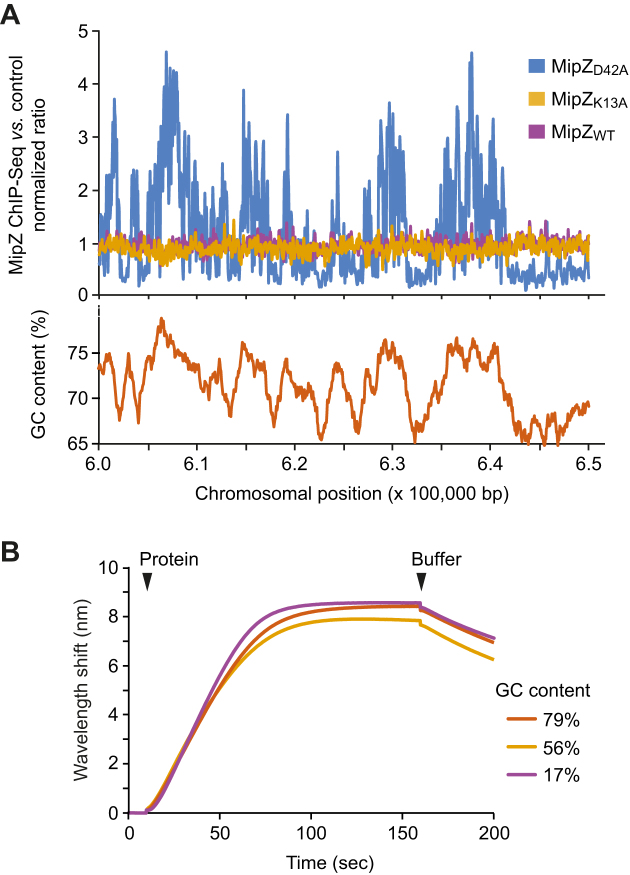
Figure 3.
Global distribution of chromosomal MipZ binding sites. (A) ChIP-seq analysis of the distribution of different MipZ variants across the C. crescentus chromosome. Cells producing a wild-type (BH64), monomeric (K13A; BH100) or dimeric (D42A; BH99) MipZ-eYFP fusion in place of the native protein were fixed with formaldehyde and subjected to ChIP-seq analysis with an anti-GFP antibody. A representative 50 kb window of the chromosome is shown for visualization. Data were normalized using wild-type strain NA1000 as a reference. (B) Biolayer interferometric analysis of the interaction of MipZ with DNA of different GC content. Biotinylated dsDNA oligonucleotides with GC contents of 17% (ATrich-biotin/ATrich-rev), 56% (GC56-biotin/GC56-rev) or 79% (GCrich-biotin/GCrich-rev) were immobilized on biosensors and probed with wild-type MipZ (4 μM) in the presence of ATPγS (1 mM).