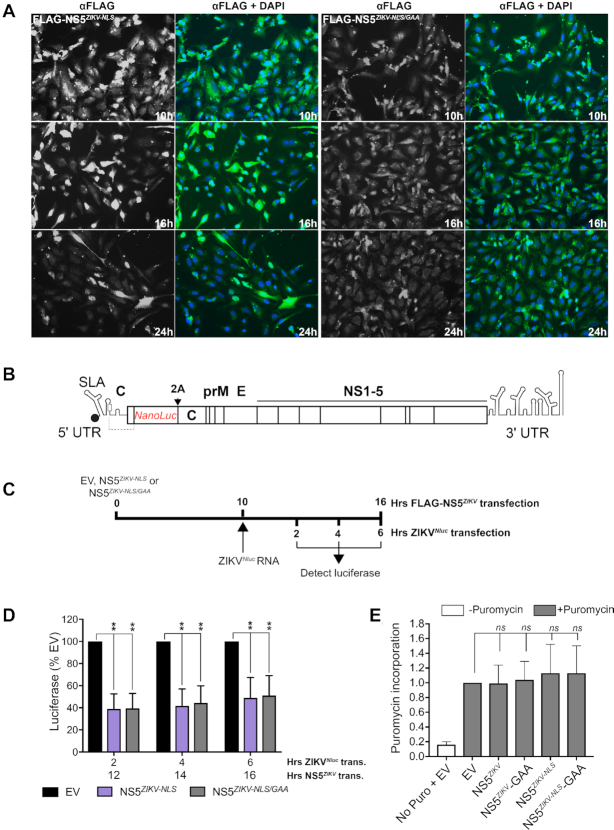
Figure 3.
NS5ZIKV inhibits viral genomic RNA translation in cells. (A) Expression of FLAG-tagged NS5ZIKV was detected by immunofluorescence using an anti-FLAG antibody over a 24 h period following transfection of Vero cells. For each FLAG-NS5ZIKV expression construct tested anti-FLAG is shown in greyscale on the left while nuclei are stained blue with DAPI and anti-FLAG is green in the associated panel to the right. (B) Schematic of the reporter ZIKV bearing nanoluciferase (Nluc) (32). The duplicate capsid sequence is separated from the marker with a 2A StopGo sequence (indicated with 2A). (C) Experimental strategy used for D. (D) Vero cells were electroporated with capped, in vitro transcribed ZIKVNluc marker RNA 10 h after transfection with the indicated FLAG-NS5ZIKV or empty vector (EV). Luciferase signal was quantified at the indicated time points. Values are normalized to the EV control at each time point and are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Time post NS5ZIKV transfection (trans.) and time post electroporation (elec.) of ZIKVNluc RNA is included on the X-axis for clarity. Statistical significance was determined by a Student's unpaired t-test with significant values indicated with an asterisk. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01. (E) Vero cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or the indicated wild type or mutant FLAG-NS5ZIKV expressing plasmids and after 10 h puromycin was added as indicated and the cells incubated for a further 2 h. Protein lysates were analysed by western blotting using an anti-puromycin antibody. The signal was quantified for each lane and normalized to that for tubulin which was used as a loading control. A representative blot is shown in Supplementary Figure S4. Data are mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Wildtype and mutant NS5 data were compared to EV by a Student's unpaired t-test and no significant change was observed.