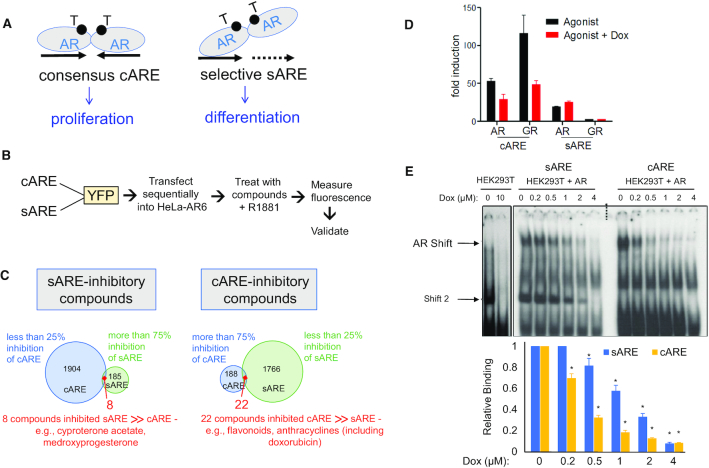
Figure 1.
Screen for compounds that act as differential modulators of AR activity, nomination of doxorubicin, and validation of AR response element selectivity. (A) Schematic illustrating the canonical AR palindromic repeat response element and selective AR response element comprised generally of half sites, both elements bound by head-to-head AR dimers. These elements are hypothesized to favor pro-proliferative versus pro-differentiative gene expression. (B) Flow chart outlining experimental steps of compound screening in HeLA-A6 cells. (C) Venn-diagram of compounds identified in the screen that specifically inhibit sARE (>75% inhibition of induced signal, with <25% inhibition of cARE signal) or cARE (>75% of signal, with <25% inhibition of sARE signal). (D) cARE or sARE driven reporters were transiently co-transfected with AR or GR expression plasmids into CV-1 cells. Cells were starved 24 h in 2.5% charcoal-stripped serum (CSS) and then treated with the respective AR or GR agonists (1 nM R1881 or 1 μM dexamethasone) with 0.4 μm dox or DMSO for 24 h prior to dual luciferase assay. Shown is the average of duplicates of a representative transfection. (E) Protein–DNA interaction was determined by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA), performed with 5 μg nuclear extracts from AR-transfected HEK293T cells and 1 ng 32P-cARE or -sARE oligo probes. Reactions were mixed on ice for 10 min with varied dox concentrations and then complexes separated by electrophoresis. Top: the specific AR-ARE shift, confirmed by antibody supershift (not shown), is denoted by an arrowhead; shift 2 appears in the absence as well as presence of AR and thus is due to non-AR factors. Bottom: histogram indicating image density from scans of three independent experiments. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) (* indicates P < 0.05 compared to both the relative control and within each condition).