Figure 7.
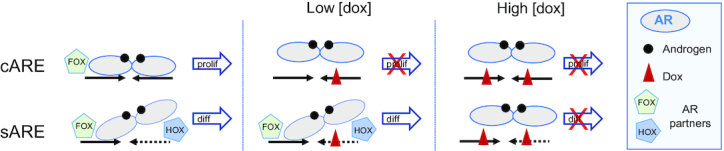
Model of the dose-dependent effects of dox on AR-signaling. AR activity without dox drives both cARE and sARE elements, promoting both proliferation (prolif) and differentiation (diff). With low dox, cARE elements are more sensitive to disruption by dox intercalation into the DNA, while sARE-driven AR activity is maintained or even enhanced by stabilizing interactions with proteins such as FOXA1, HOXB13 and NKX3.1 (FOX, HOX – AR partners), perhaps freed from binding at cARE elements. Low dose dox thus will promote differentiation from sAREs, while inhibiting proliferation at cAREs. Finally, at high doses dox intercalates into more regions of the genome, ultimately disrupting all transcription, including that which is mediated by AR.
