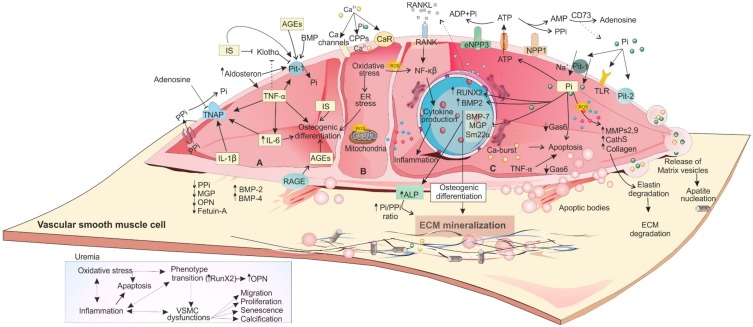
Figure 2.
The impact of uremic toxins on CKD-induced VSMC dysfunction and VC. Due to hyperphosphatemia, hypercalcemia, elevated oxidative stress, and inflammation,132 VSMCs manifest dysregulated functions and phenotype. Uremic toxins including Pi, IS, AGEs, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α are involved in CV. (A) IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α induce osteoblast-like trans-differentiation of VSMCs through different mechanisms.16 Interaction of AGEs with their receptor (RAGE) induces the expression of Pit-1 via ROS production49 and leads to osteogenic transition. It also causes apoptosis through NAD(P)H oxidase-derived oxidative stress.133 (B) In CKD, normal Ca homeostasis is also dysregulated. This homeostasis is mediated by klotho, PTH, active vitamin D metabolites, and calcitonin. In VSMCs, Ca signaling is mediated by Ca channels, CaR, and pumps that maintain Ca concentrations in these cells.134 Higher level of extracellular Ca is associated with the release of MVs and cell death promotion and release of apoptotic bodies.43 (C) Extracellular Pi, as a signaling molecule, can trigger numerous changes in VSMCs through regulating different molecular pathways. NPP1 is responsible for extracellular ATP degradation to AMP and PPi, CD73 degrades AMP to adenosine and Pi and TNAP breaks PPi into phosphate and adenosine.15 Higher Pi level simultaneously upregulates the expression of osteo/chondrogenic genes (Runx2, ALP, OPN, and osterix) and downregulates VSMCs genes (SM22α and αSMA). ALP controls vascular matrix mineralization by degradation and inactivation of the VC inhibitors (PPi and P-OPN) to allow uncontrolled tissue mineralization and simultaneously releasing free Pi.43 These osteo-/chondroblast-like cells actively induce apoptosis and vesicle release, a reduction in calcification inhibitors, elastin degradation, increased ECM remodeling, and a pro-inflammatory state. Moreover, under high levels of Pi, VSMCs synthesize collagen at high amount and provide a collagen-enriched ECM. Downregulation of Gas6 and Bcl2 may be the basic mechanism of VSMCs apoptosis. The released apoptotic bodies provide a further nidus for deposition of Pi and Ca. For more details, see the full text.
Abbreviations: Ca, calcium; Pi, phosphate; PPi, pyrophosphate; ECM, extracellular matrix; MMP, matrix metalloproteinases; Gas6, growth arrest-specific gene 6; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SM, α-smooth muscle actin; CPPs, calciprotein particles; CaR, Ca sensing receptor; MVs, matrix vesicles; AGEs, advanced glycation end products; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products.