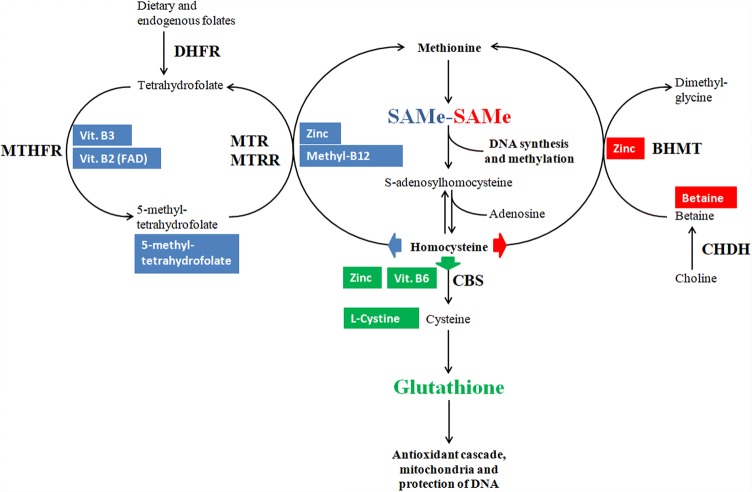
Fig. 1.
Rationale for homocysteine removal by the administration of a full array of activated micronutrients. The one carbon cycle is regulated by the availability of its substrates; accordingly, a wider availability of each substrate may enhance its performance. Blue background substrates: Folates, B12, chelated zinc, Vit. B2 and Vit. B3 feed homocysteine re-methylation by the folate pathway; Folates in the form of methylfolate escape possible genetic defects in the activity of DHFR and MTHFR; B12 in the form of methylcobalamin escapes possible genetic defects in the activity of MTRR. Red background substrates: Betaine and chelated zinc feed homocysteine re-methylation by the betaine pathway; Pre-formed betaine escapes possible genetic defects in the activity of CHDH and provide an excess of substrate for the BHMT reaction. Green background substrates: Vit. B6, chelated zinc and cysteines feed homocysteine transsulfuration to glutathione (GSH); Excess of cysteines downstream to CBS reaction ensure GSH production even in case of genetic defects of CBS. Key enzymes subject to genetic variability: DHFR DiHydroFolate reductase, MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, MTR methionine reductase (methionine synthase), MTRR methionine synthase reductase, CBS cystathionine beta synthase