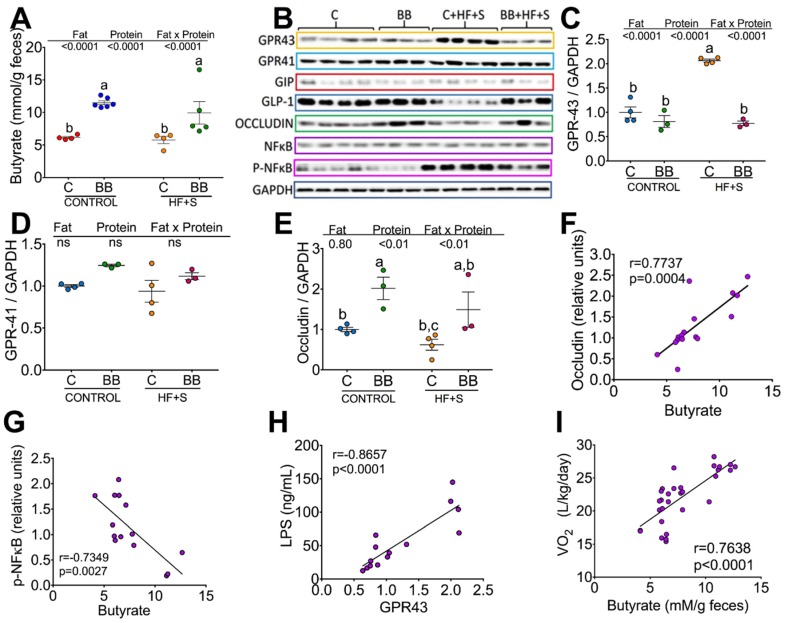
Figure 4.
Consumption of black bean increases butyrate and decreases NF-κB protein abundance in the colon. (A) Fecal butyrate concentration, (B) Western blot analysis of G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 41 and 43, occludin, NF-κB, P-NF-κB, (C–E) and densitometric analysis of GPR41, GPR43 and occludin after 2 months of dietary treatments with casein [C], black bean [BB], Casein + high-fat + S 5% [C + HF + S], BB + HF + S. (F) Correlation between occludin and butyrate, (G) correlation between NF-κB and butyrate, (H) correlation between LPS and GPR43. (I) correlation between VO2 and fecal butyrate concentration.