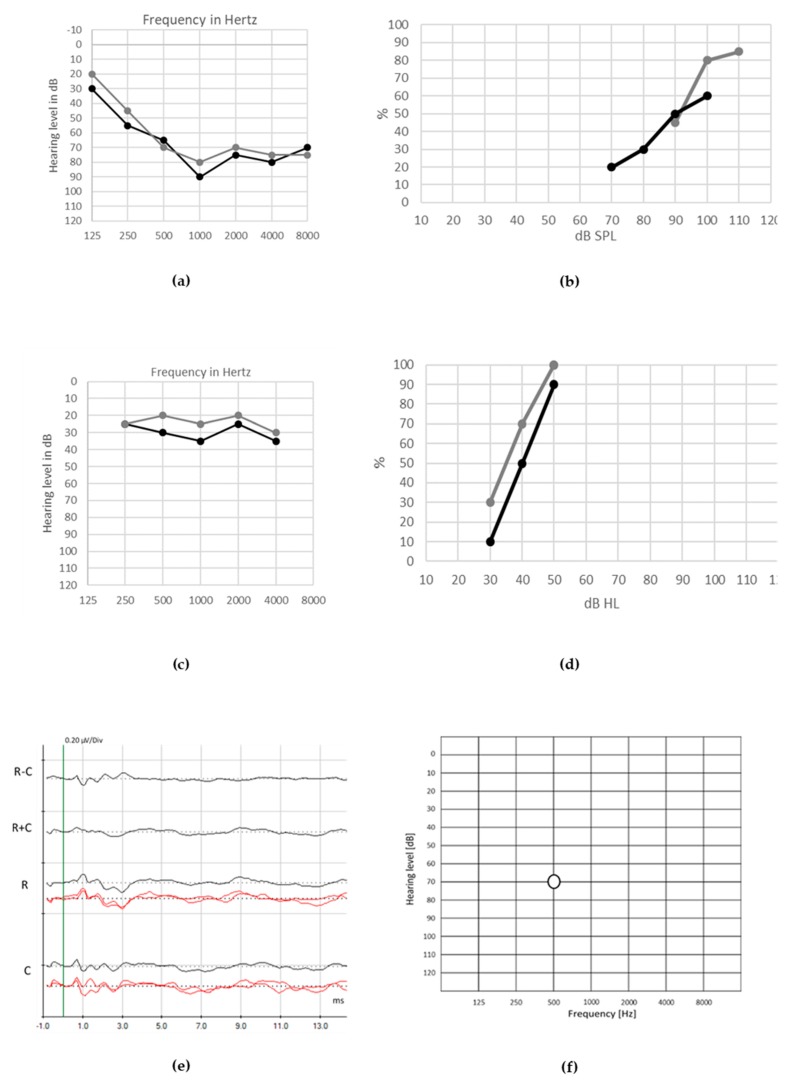
Figure 8.
Audiological assessment in a 14-year-old child with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder (ANSD) features occurring with severe hearing loss. Her medical history includes a 35-week preterm birth after an intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, with normal birth weight but neonatal hypoxia requiring 3 weeks of stay in neonatal intensive care unit. Hearing aids were fitted in early infancy. Besides poor sounds recognition and speech perception, speech development was good in the lexical and morphosyntactic fields. Unaided tonal thresholds ((a), gray line for right ear, black line for left ear) and unaided speech discrimination (b) are poor. Aided pure-tone audiometry (c) and speech perception (d) with hearing aids are clearly improved, allowing a good development of language skills and learning abilities. Auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) elicited by clicks at 90 dB show small cochlear microphonic (CM) (e). Auditory steady-state responses (ASSRs) (f) are detected for 500 Hz at the right ear.