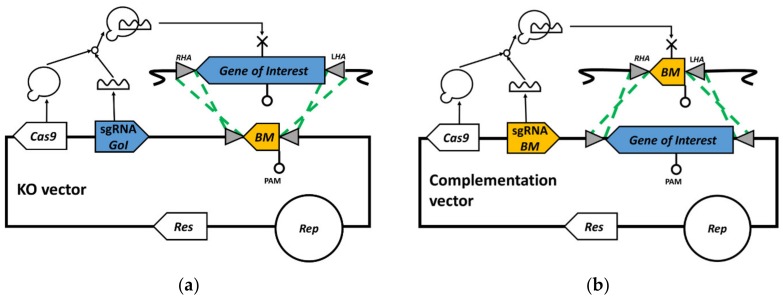
Figure 1.
Overview of the bookmark complementation strategy. (a) First step—knockout of the gene of interest and insertion of the bookmark in its genomic locus using a knock-out vector consisting of a Cas9 nuclease and single guide RNA (sgRNA) expression cassettes, as well as an editing template composed of one 24 nucleotides (nt) bookmark flanked by homology arms. (b) Second step—after isolation of the knockout (KO) mutant and plasmid loss, another round of Cas9-mediated homology-directed mutagenesis is carried out with the help of a complementation vector, to restore the gene of interest in its original locus. The complementation vector is identical to the KO vector, except for its sgRNA cassette, which targets the genomic bookmark that was previously inserted, and editing template, which consists of the gene of interest flanked by the same homology arms. The gene of interest can be watermarked with a silent mutation for higher reliability of the complementation step. GoI: Gene of interest, Res: Antibiotic resistance marker, Rep: Replicon, BM: Bookmark, LHA: Left homology arm, RHA: Right homology arm.