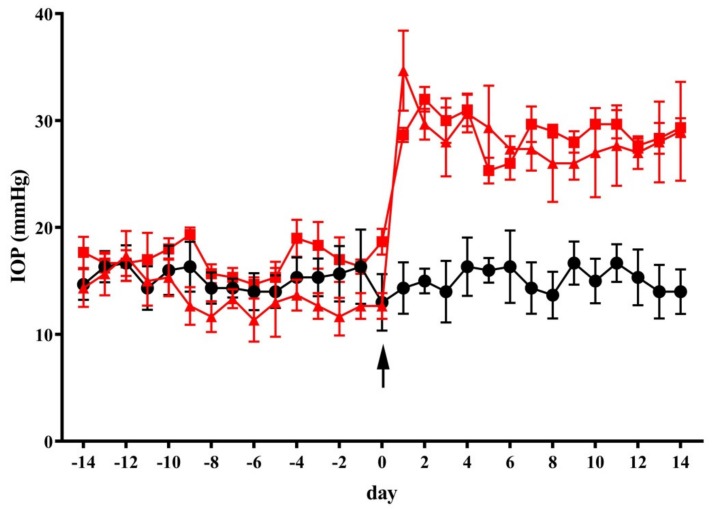
Figure 1.
Dietary supplementation did not affect intraocular pressure (IOP). The injection of methylcellulose (MCE) in the anterior chamber at day 0 (arrow) resulted in a significant elevation in the intraocular pressure. Both the vehicle and diet supplement did not affect IOP in mice receiving MCE. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 11 for each group). Black circles and line: control mice; red squares and line: mice intraocularly injected with MCE fed with vehicle; red triangles and line: mice intraocularly injected with MCE fed with diet supplement.