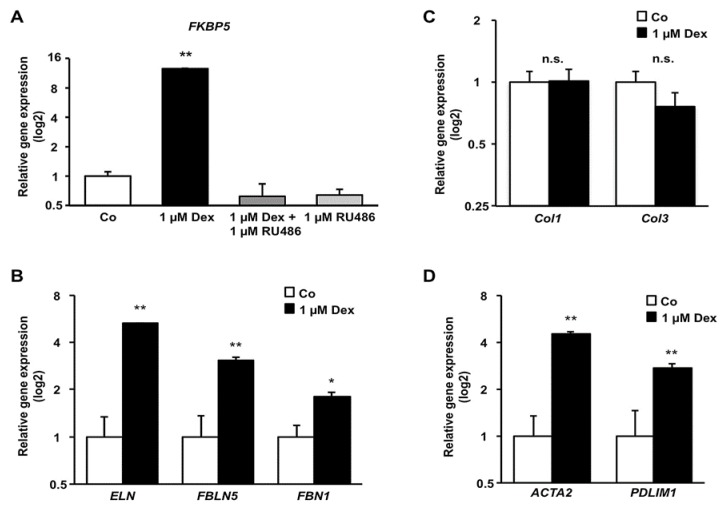
Figure 4.
Dex treatment of HTPCs rapidly increases FKBP5 mRNA, a known target of GR signaling, and affects mRNA levels of characteristic peritubular ECM markers, as well as cytoskeleton-associated genes. (A) Cultured HTPCs stimulated with Dex (1 µM) in the absence or presence of RU486 (1 µM), respond with a highly significantly increase (p < 0.01) in FKBP5 mRNA levels after 6 h compared to control. RU486 completely blocks this effect (p < 0.01) and does not alter FKBP5 mRNA expression within 6 h. (B) After Dex treatment of HTPCs for 24 h, the mRNAs of the elastic fiber components ELN and FBLN5 are highly significantly (p < 0.01) increased. A slightly smaller (p < 0.05) increase is observed for FBN1 mRNA. (C) The transcript concentration of the collagen fibers Col1 and Col3 do not change (p > 0.05) after application of Dex, while (D) the mRNAs of cytoskeleton markers ACTA2 and PDLIM1 (n = 8) are enriched (p < 0.01) after stimulation of HTPCs with Dex. Data are means ± SEM after 6 (A), and 24 h (B–D), normalized to control conditions. Asterisks denote statistical significance, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.