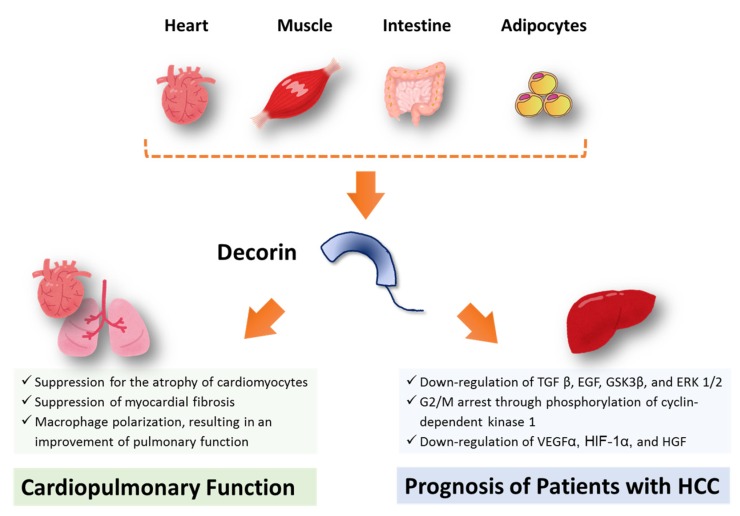
Figure 3.
A scheme for the proposed hypothesis of this study. Decorin is expressed in various tissues including skeletal muscle, heart, intestine, and adipocytes. In this study, it remains unclear where decorin comes from. Decorin may be associated with cardiopulmonary function, because decorin suppresses the atrophy of cardiomyocytes, myocardial fibrosis, and causes macrophage polarization. In addition, decorin may be associated with prognosis of patients with HCC, because decorin downregulates transforming growth factor-β1, epidermal growth factor receptor, glycogen synthase kinase 3β, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, G2/M arrest through phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1, downregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α, and hepatocyte growth factor. Abbreviations: TGF β, transforming growth factor-β1; EGF, epidermal growth factor receptor; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; and ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor.