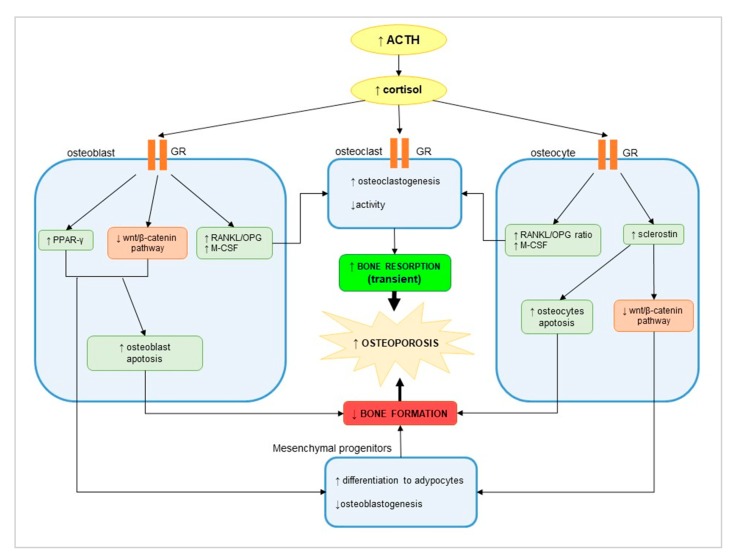
Figure 3.
Direct effect of cortisol excess due to ectopic ACTH secretion on bone health: osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts express glucocorticoid receptors (GRs), which mediate the cortisol action. Cortisol excess induces the secretion of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ and inhibits the wnt pathway, inducing osteoblast apoptosis and differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors into adipocytes. On the other side, Sclerostin induces osteocyte apoptosis and inhibits the wnt pathway. These mechanisms inhibit bone formation. The increase of the receptor activator for NF-κB ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) ratio, together with the increased macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Decrease of bone formation and increase of bone resorption leads to osteopenia/osteoporosis.