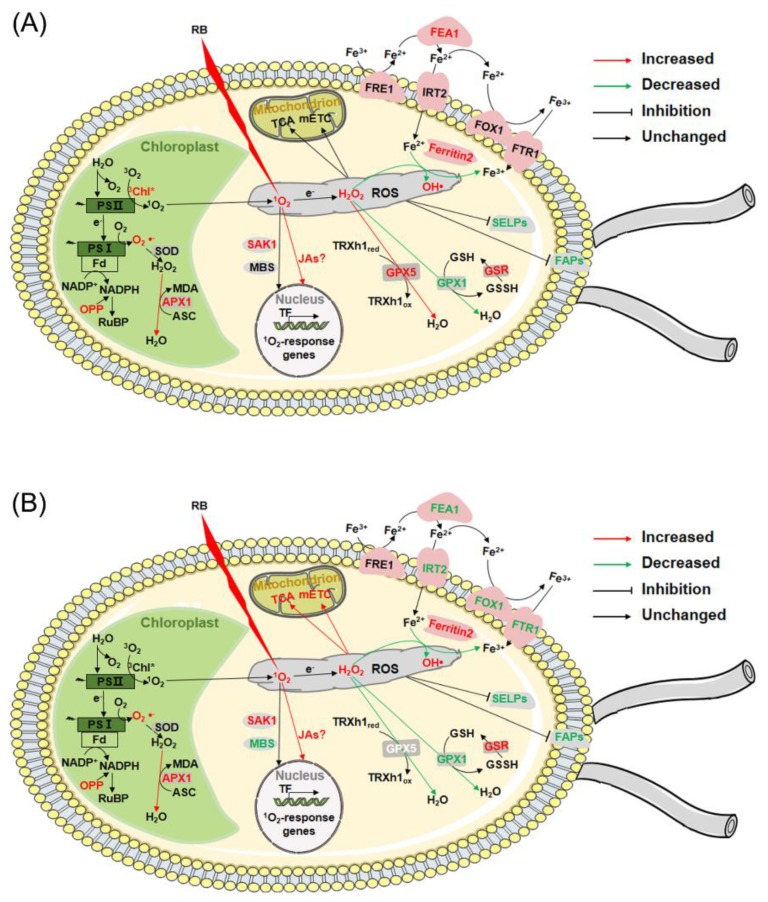
Figure 7.
Summary of the cellular response to oxidative stress in CC4348 (A) and the gpx5 mutant (B). (A) After treatment with RB, the CC348 cells upregulated the ROS detoxification system and inhibited the expression of flagellar associated proteins (FAPs) and selenoproteins (SELPs). (B) When the gpx5 mutant suffered the treatment with RB, expect for the same responses of ROS detoxification system, FAPs and SELPs, several specific responses occurred, such as accelerated the TCA cycle and mETC in mitochondria, repressed genes related to chlorophyll metabolism and photosynthesis, and downregulated iron transporters. Red characters indicate upregulated expression of related proteins or metabolic pathways after RB treatment, while green characters indicate downregulated expression of related proteins or metabolic pathways after RB treatment. Abbreviations: APX, ascorbate peroxidase; ASC, ascorbate; FAPs, flagellar associated proteins; Fd, ferredoxin; FEA1, Fe-assimilating protein 1; FOX1, ferroxidase; FRE, ferrireductase 1; FTR1, ferric ion transporter 1; GPX, glutathione peroxidase; GSR, glutathione reductase; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; IRT2, ferrous ion transporter 2; mETC, mitochondrial electron transfer chain; OPPP, oxidative pentose phosphate pathway; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PRX, peroxiredoxin; PSI/II, photosystem I/II; RB, rose bengal; RuBP, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate; SELPs, selenoproteins; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TF, transcription factor; TRXh1, thioredoxin h1. SAK1 [17] and MBS [16] are two cytosolic proteins required for induction of nuclear gene expression responses by 1O2.