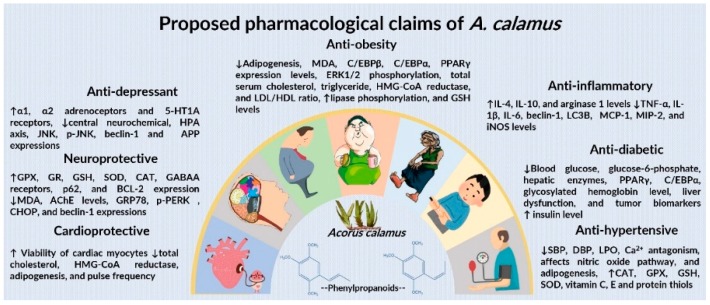
Figure 6.
Illustration of role of A. calamus mechanisms in the treatment of neurological and metabolic disorders. AChE, acetylcholinesterase; APP, amyloid precursor protein; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; CCAAT (cytosine-cytosine-adenosine-adenosine-thymidine)-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; C/EBP, CCAAT enhancer-binding protein; GABAA, γ-Aminobutyric acid type A; GRP78, 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; JNK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; LC3b, microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B; MCP, modified citrus pectin; MDA, malondialdehyde; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; p-PERK, phospho-protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase.