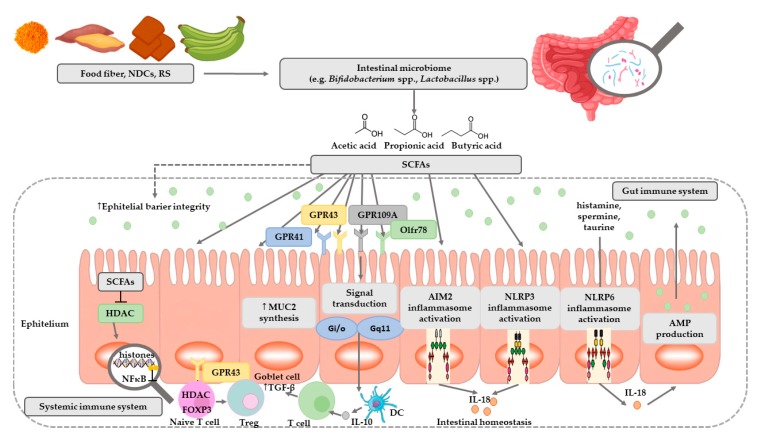
Figure 2.
The role of SCFAs in regulation of intestinal homeostasis. SCFAs (acetic, propionic, and butyric acid) are produced by intestinal microbiome in fermentation of undigested food fiber, non-digestible carbohydrates (NDCs) or resistant starch (RS). SCFAs are as energy substrates for colonocytes and regulate intestinal barrier function (synthesis of mucin-MUC2) and immune system through G-protein-coupled receptors (GPR41, GPR43, GPR109A) and Olfr78 receptor signaling. SCFAs regulate the histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity which affects inhibition of nuclear factors (nuclear factor-κB; NF-κB). SCFAs affect the differentiation of regulatory T (Treg) cells and the production of interleukin-10 (IL-10) with the participation of GPR43. SCFAs also regulate dendritic cell (DC) function. In addition, SCFAs influence AIM2 and NLRP3 inflammasomes activation which then affects production of interleukin-18 (IL-18) and enhanced epithelial barrier function. Moreover, NLRP6 inflammasome activation and secretion of IL-18 regulate the production of intestinal antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) [54,55]. Abbreviations: FOXP3-forkhead box P3; TGF-β-transforming growth factor β.