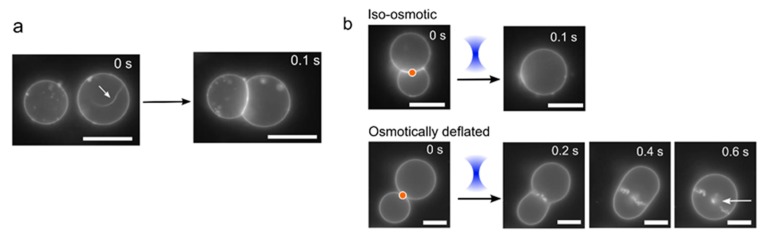
Figure 4.
Vesicle morphology changes under different osmotic conditions. (a) If vesicles have excess membrane area and low tension, they may contain tubules (white arrow). Upon adhesion, the vesicle deform to a non-spherical geometry, which increases its tension and leads to a retraction of the tubule into the main vesicle body. (b) Images showing post-fusion morphologies under iso-osmotic (0.75 M sucrose internally; 0.35 M glucose, 0.2 M NaCl externally) and osmotically deflated (0.75 M sucrose internally; 0.4 M glucose, 0.2 M NaCl externally; low tension) conditions. In the former, a clean-merge is seen; in the latter the vesicle slowly relaxes to a spherical shape and many smaller internal vesicles are produced and retained inside (white arrow). Orange dot corresponds to area of laser focus. Scale bars = 5 µm.