Table 1.
Structure of the main flavonoid compounds. Based on their structural differences, flavonoids can be divided into flavones, flavonols, flavanones, isoflavonoids, flavanols, and anthocyanins. Flavonoids whose epigenetic action is detailed in the text are in bold.
| Chemical Structure | Bonds | Compounds | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLAVONES |
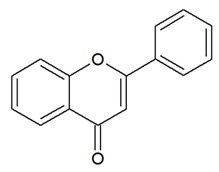
|
Double bond between C2-C3 and a ketone in C4 of the C ring. | Apigenin Luteolin Morin Tricin |
| FLAVONOLS |
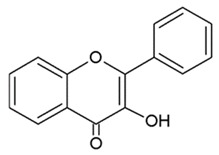
|
Hydroxylic group, a double bond between C2-C3 and a ketone in C ring. | Quercetin Myrecitin Fisetin Kaempferol |
| FLAVANONES |
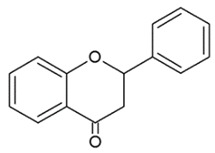
|
Lack the double bond between C2-C3 in C ring; only hydroxyl and methoxy groups as substituents. | Silibinin Naringenin Hesperdin |
| ISOFLAVONOIDS |
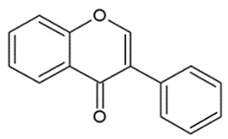
|
Large diversity of structure in the C ring. The B ring is attached at C3 rather C2 of the C ring. | Genistein DaidzeinGlycitein |
| FLAVANOLS OR CATECHINS |
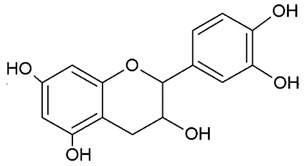
|
No double bond of C2-C3 in the hydroxyl group in position 3. | EGCG Epicatechin Epicatechin-3-gallate |
| ANTHOCYANINS |
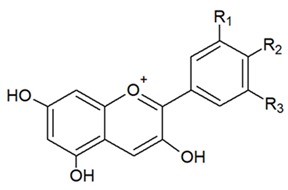
|
Flavylium cation binding hydroxyl groups and/or methoxy group(s) in R₁, R₂, and R₃ position. | Delphinidin Cyanidin PeonidinN |
