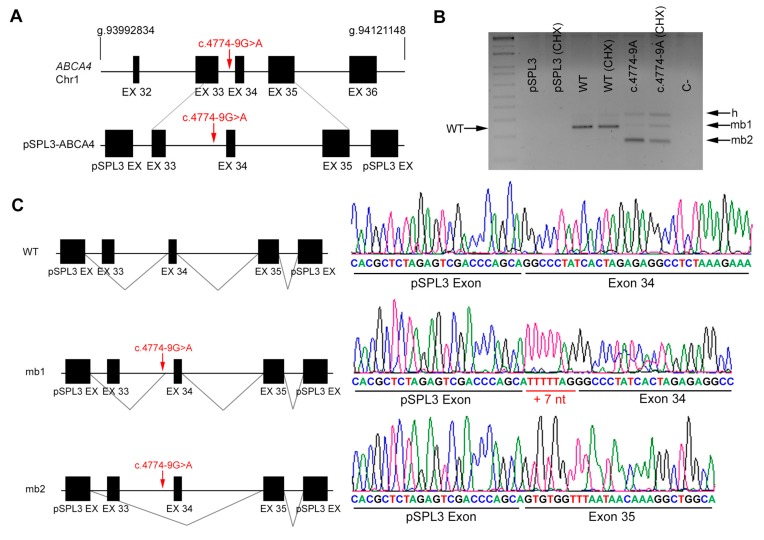
Figure 2.
In vitro splicing analysis of the non-canonical splice site (NCSS) variant identified in ABCA4 in patient DBG1. (A) Genomic position of the identified NCSS variant in intron 33 of the ABCA4 gene (c.4774 -9G>A). Diagram showing the genomic region amplified from patient’s DNA, cloned into the pSPL3 vector. Note that exon 33 was not included in full. (B) Analysis of ABCA4 mRNAs from HEK293T cells transfected with either empty vector, WT or mutant genomic sequences (treated or untreated with cycloheximide, CHX). The band of 247 bp corresponds to the wild-type transcript (WT), whereas cells transfected with pSPL3 carrying the NCSS variant produced two different aberrant transcripts (mb1 and mb2). h indicates the heteroduplex band of mb1 and mb2. C- indicates the PCR negative control. (C) Subsequent Sanger sequencing of cloned individual bands (indicated in the left diagrams) and comparison to the wild-type transcript confirmed the insertion of 7 bp from intron 33 (mb1) due to acceptor splice site shift as well as exon skipping of exon 34 (mb2).