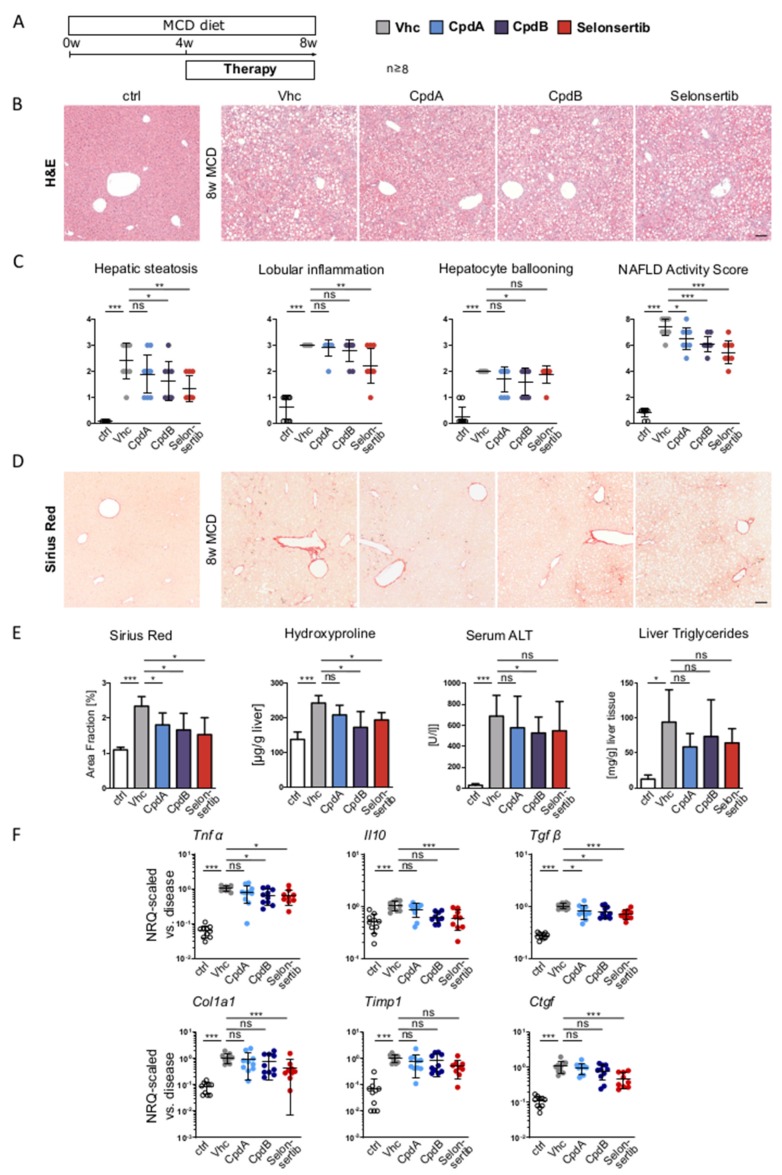
Figure 4.
Pharmacologic inhibition of GPR84 ameliorates steatohepatitis and fibrosis in MCD diet-induced fatty liver disease. (A) Mice (n ≥ 8) were fed with a methionine choline deficient (MCD) diet for a period of 8 weeks. Oral pharmacological therapy was conducted over the last 4 weeks of liver injury induction with the two GPR84 antagonists (30 mg/kg BW, PO q.d.) and Selonsertib (15 mg/kg BW, PO b.i.d.) as a positive control. (B) Liver histology was evaluated based on H&E stainings, showing severe fibrosing steatohepatitis in MCD fed animals. (C) The NAFLD activity score (NAS) was assessed by an external expert pathologist (Histalim), revealing a significantly reduced NAS upon GPR84 or ASK1 inhibition. (D) Liver fibrosis was assessed by Sirius-Red-stained liver sections (red: extracellular matrix deposition). (E) Quantification of liver fibrosis by Sirius-Red-stained areas and hepatic hydroxyproline content, liver injury by serum ALT and steatosis by hepatic triglyceride concentrations. (F) Inflammation- and fibrosis-related gene expression in total liver measured by RT-qPCR. All images were taken at ×10 magnification; scale bar, 100 µm. Data are presented as mean ± SD based on n ≥ 8 per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA). Abbreviations: CpdA/B, compound A/B; Vhc, vehicle; Tnfα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; Il10, interleukin 10; Tgfβ, transforming growth factor beta; Col1a1, collagen type I, alpha 1; Timp1, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1; and Ctgf, connective tissue growth factor.