Figure 3.
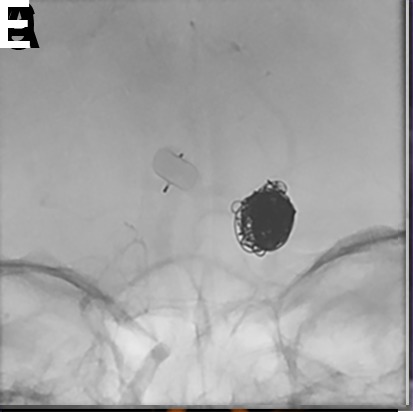
(A) A patient with a prior history of subarachnoid hemorrhage caused by rupture of a posterior communicating artery aneurysm presented for WEB treatment of an enlarging unruptured basilar apex aneurysm. (B) Post-deployment native digital subtraction angiogram (DSA) demonstrating adequate positioning of the WEB SL within the aneurysm. (C, D) Post-detachment native DSA demonstrating change in orientation of the deployed WEB device causing mild impingement of the left posterior cerebral artery. A decision was made to deploy a LVIS stent (MicroVention, Terumo, Tustin, California, USA) to protect the left posterior cerebral artery. (E, F) Post-deployment flat panel cone-beam CT with reconstruction of the LVIS stent showing the WEB device within the aneurysm and patent LVIS stent spanning from the left posterior cerebral artery into the basilar artery.
