FIGURE 3.
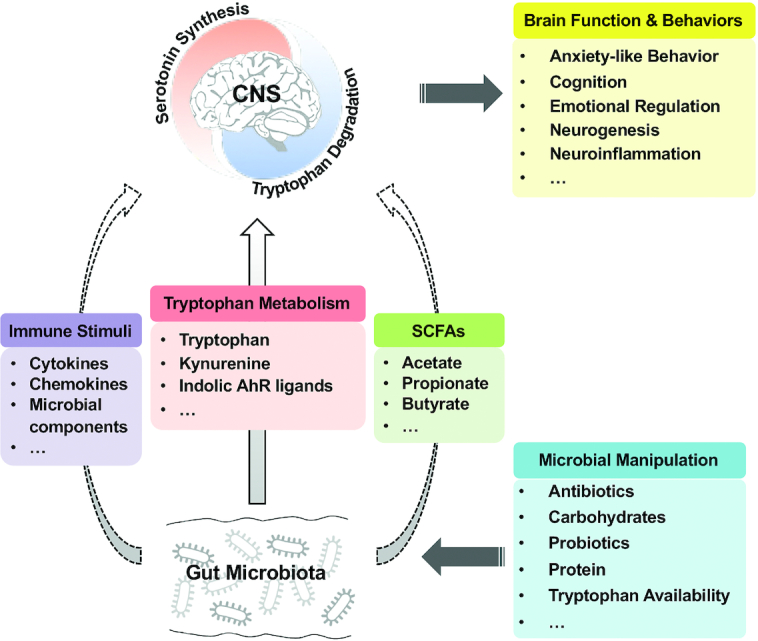
The potential role of tryptophan metabolism in the gut microbiota-brain axis. Manipulations of gut microbiota composition and metabolism by various ways (e.g., antibiotics and probiotics) contribute to the shifts in the central tryptophan metabolism between serotonin synthesis and tryptophan degradation pathways, which thereby influence the brain function and behaviors. The solid arrow indicates the tryptophan metabolism–dependent effects of alterations in gut microbiota on the central tryptophan metabolism; the dashed arrow indicates the tryptophan-independent effects on the central tryptophan metabolism. AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CNS, central nervous system; SCFA, short-chain fatty acid.
