Fig. 2 |. Characterization of the GR-MN.
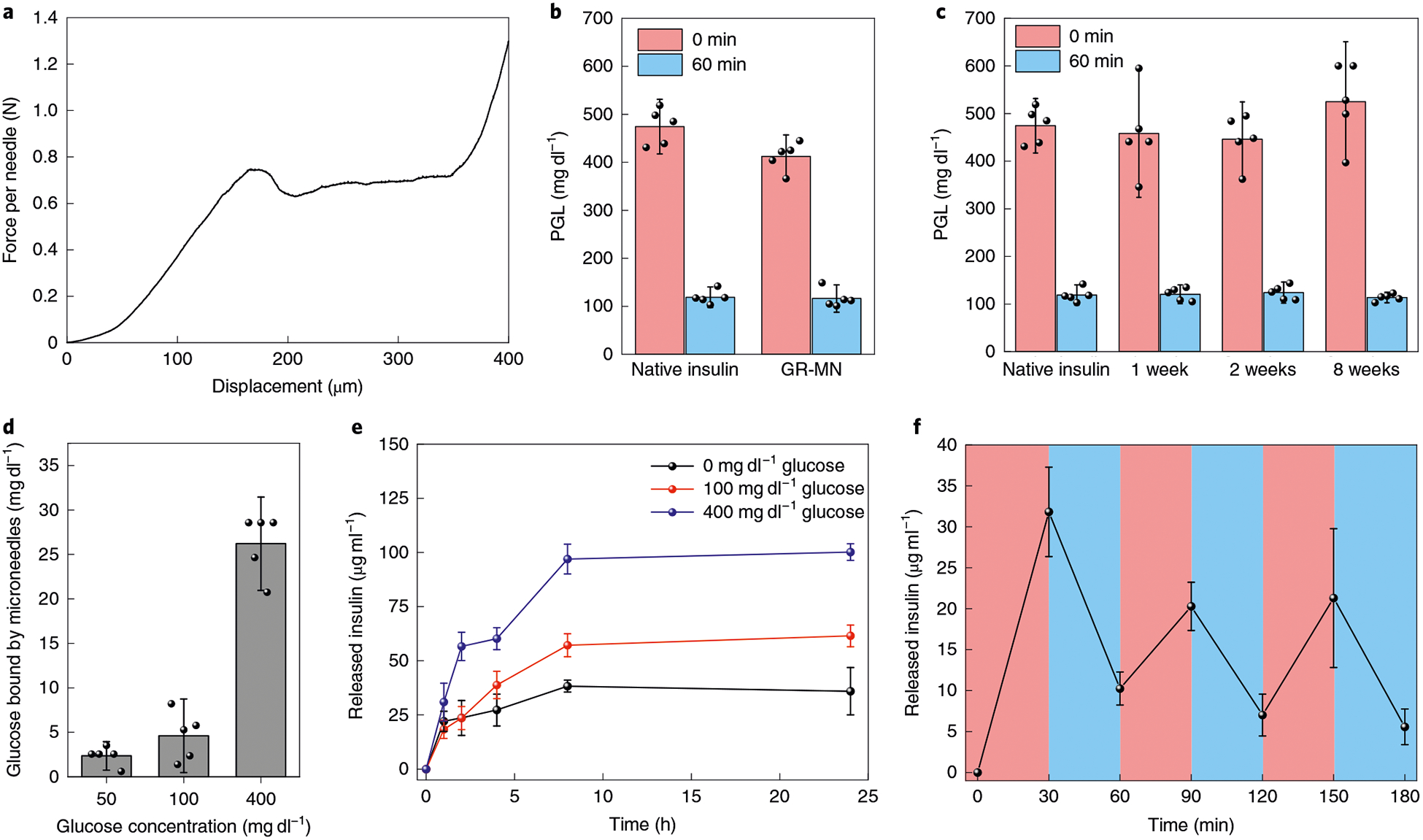
a, Mechanical behaviour of the GR-MNs. b, Glucose-lowering activity of the insulin extracted from the freshly prepared patch in diabetic mice (n = 5). Initial glucose levels were compared with glucose levels at 60 min post-injection of insulin solution. c, Glucose-lowering activity of the insulin extracted from the patches stored at room temperature in diabetic mice (n = 5). d, Glucose concentration-dependent glucose-binding capability of the glucose-responsive polymeric matrix (n = 3). e, In vitro accumulated insulin release of the glucose-responsive polymeric matrix (n = 3) in several glucose concentrations at 37°C. f, Pulsatile release profile showing the rate of insulin release from the glucose-responsive polymeric matrix (n = 3) as a function of the glucose concentration (blue: 100 mgdl−1; red: 400 mgdl−1). Inb-f, data are presented as mean ± s.d.
