Fig 1.
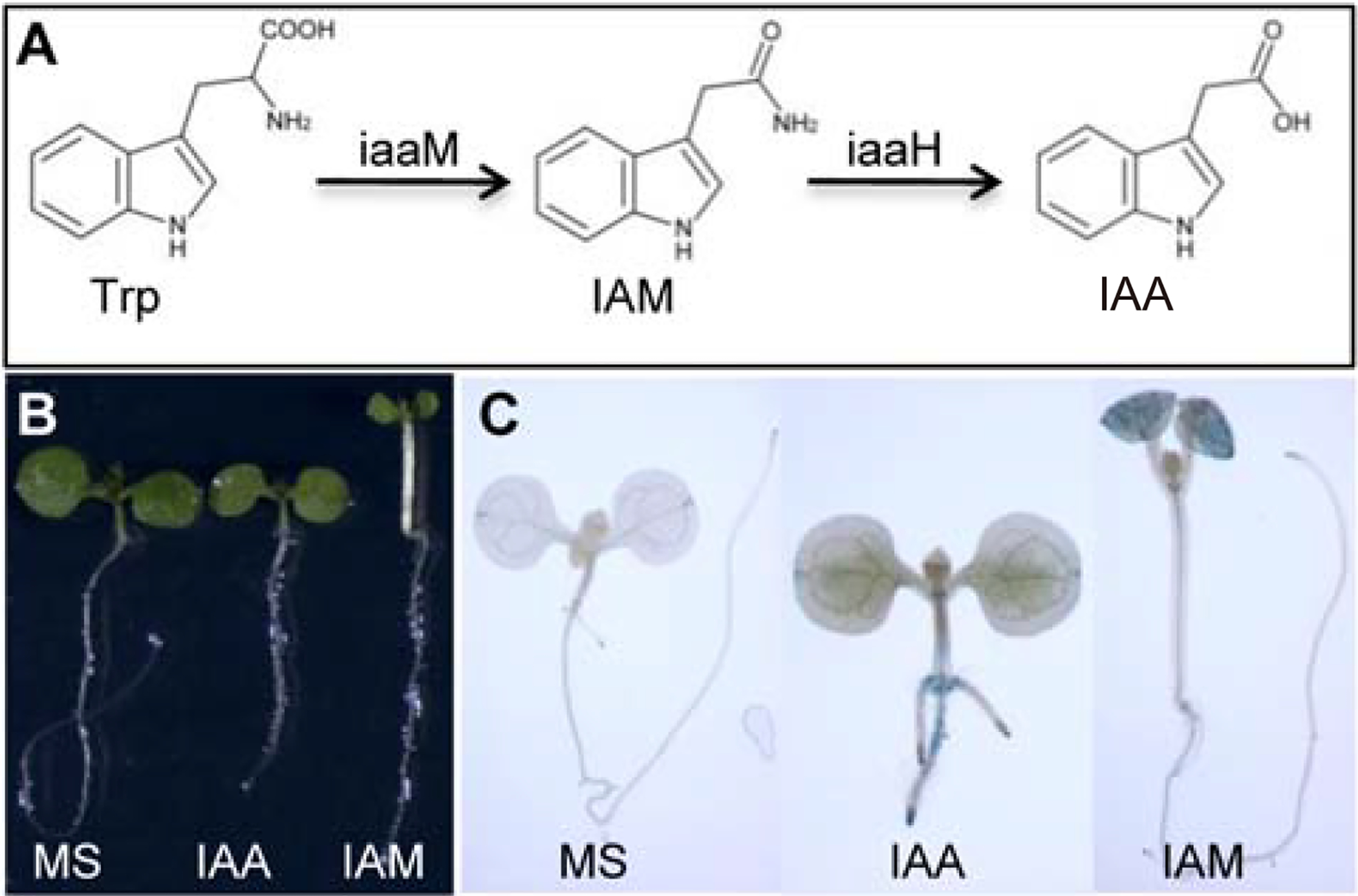
Indole-3-acetamide (IAM) is a potential auxin biosynthetic intermediate in plants and IAM treatments affect plant growth and activate the auxin reporter DR5-GUS. A: A proposed Trp-dependent auxin biosynthetic pathway using IAM as the intermediate. This pathway is used by plant pathogenic bacteria such as Agrobacteria, which uses the iaaM and iaaH genes to convert Trp to IAA. The roles of IAM in plant auxin biosynthesis are not clear. B: Five-day old Arabidopsis seedlings grown on MS media and media containing 20 μM IAA or IAM. Note that IAA inhibits primary root elongation and IAM stimulates hypocotyl growth. Note that the seedling above the label IAA and IAM refer to seedlings grown on IAA and IAM-containing media, respectively. C: Activation of DR5-GUS expression by IAA and IAM. Interestingly, IAM mainly activates DR5-GUS expression in aerial tissue whereas IAA increases DR5-GUS signal in the root.
