Figure 1.
Efficient Neutralizing Antibody Identification through Antigen-Enriched High-Throughput Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
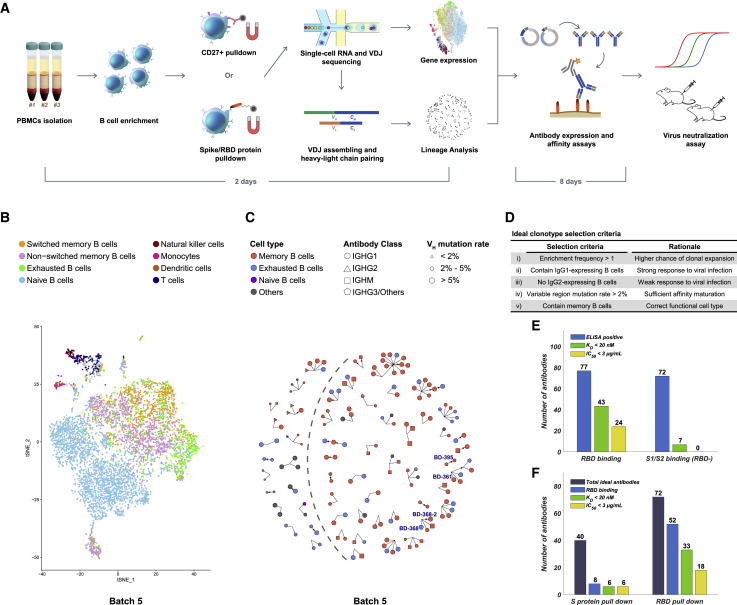
(A) Schematic overview of the neutralizing antibody identification process. The sequence of the mAbs could be obtained within 2 days using 10X Genomics 5′ VDJ sequencing.
(B) Cell-type identification of the single B cells binding RBD (batch 5) based on gene expression. Only productive heavy-light chain-paired single cells are analyzed. See also Figures S1 and S2.
(C) Ideal clonotype selection for in vitro expression showing clonotype’s enrichment frequency, immunoglobulin class, cell type, and variable region mutation rate (batch 5). Ideal clonotypes are on the right side of the dashed line with four potent neutralizing mAbs selected for further characterization are labeled.
(D) Ideal clonotype selection criteria.
(E) Characteristics of RBD-binding and spike-protein binding (RBD-) antibodies. Only RBD-binding antibodies showed neutralizing ability in pseudovirus neutralization assays. An antibody was determined as ELISA positive if it showed saturated absorption at 1 μg/mL antigen and 1 μg/mL antibody concentration. KD was measured by using SPR with a 1:1 binding model.
(F) Characteristics of the antibodies selected based on different antigen enrichment methods.
See also Figure S3.