Figure EV1. Analysis of the role of ydcA in the phenotypic behaviour of Bacillus subtilis during Mn stress.
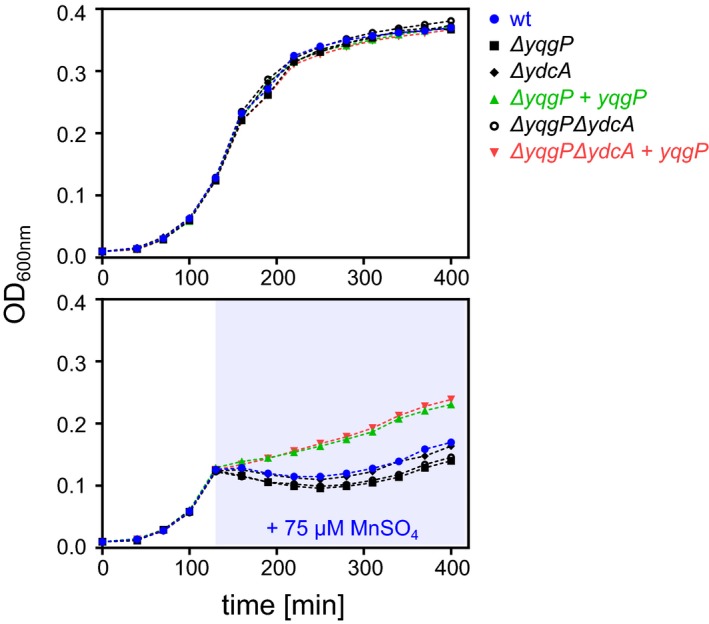
Growth curves of wild‐type (BTM843, Table EV2), yqgP‐deficient (BTM844, Table EV2), ydcA‐deficient (BTM1001, Table EV2), yqgP ydcA‐deficient (BTM1003, Table EV2) and YqgP rescue (BTM845 and BTM1005, Table EV2) strains of B. subtilis in M9 minimal medium with limiting magnesium (0.01 mM MgSO4), exposed to manganese stress elicited by adding 75 μM MnSO4 in mid‐exponential phase (stress phase denoted by blueish background, in bottom panel). All strains further contain a deletion in the putative manganese efflux pump MntP (ΔywlD, Table EV2). Bottom panel shows that manganese is more toxic in both yqgP‐deficient strains (black squares or open black circles) than in the wild type or ydcA rhomboid‐deficient strains. The overexpression of YqgP in both ΔyqgP and ΔyqgPΔydcA strains rescues fitness during manganese stress to above wild‐type level. Top panel shows no difference between the strains in the absence of manganese stress.
