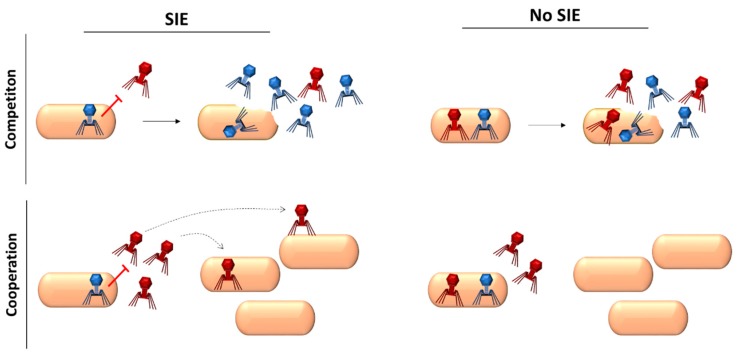
Figure 4.
Two possible evolutionary interpretations of superinfection exclusion (SIE). Superinfection exclusion could be considered as a mechanism for avoiding competition for intracellular sources. In this scenario, superinfection exclusion would directly increase the fitness of the actor virus, which would capitalize on cellular resources at the expense of the excluded virus. Alternatively, superinfection exclusion could be considered as a cooperative mechanism whereby the actor virus would pay the cost of promoting the spread of the excluded virus (indicated by dotted arrows) to uninfected neighbor cells, which would improve overall resource exploitation.