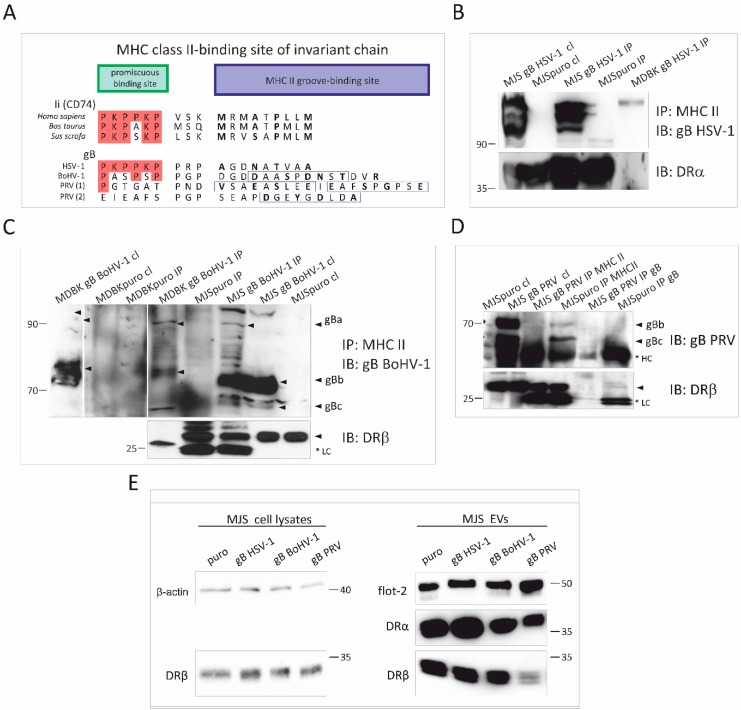
Figure 5.
Analysis of interaction between MHC II and HSV-1, BoHV-1 or PRV gB, and the effect of alphaherpesvirus gB on MHC II incorporation in EVs. (A) Comparison of amino acid sequences representing potential HSV-1, BoHV-1, and PRV gB and MHC II biding site. HSV-1 gB contains an allotypic HLA-DR-binding region homologous to the human invariant chain (Ii, CD74), consisting of the promiscuous and the MHC II groove-binding sites. Whereas bovine and porcine Ii sequences are highly conserved, their corresponding regions in BoHV-1 and PRV gB (two candidate sequences) are variable. Amino acids (aa) that are identical to those in human Ii are in red frames. Boxes highlight predicted MHC II peptides. The groove-binding positions are in bold. (B) Complex formation between HSV-1 gB and HLA-DR or bovine MHC II from cell lysates was evaluated by co-immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-MHC II mAb. Immunoprecipitated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-gB or anti-DRα antibodies (for human cells). (C) and (D) Co-IP with anti HLA-DR or bovine MHC II (in C) mAb from MJS BoHV-1/PRV gB or MDBK BoHV-1 gB lysates. gB or DRβ were detected in SDS-PAGE-separated complexes by IB. Size markers are in kilodaltons. *LC: light chain of antibodies; HC: heavy chain of antibodies. Arrows indicate gB species. (E) Detection of DRα, DRβ and flotillin-2 (flot-2) as an EVs marker in SEC-purified EVs by IB. β-actin and DRβ were detected in cell lysates for comparison. Size markers are in kilodaltons.