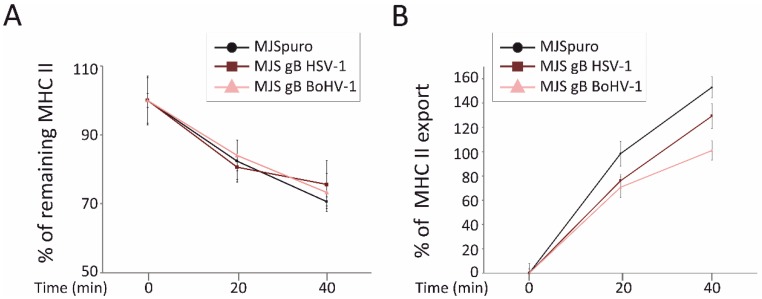
Figure 6.
HSV-1 and BoHV-1 gB do not affect internalization but contribute to a retarded appearance of MHC II at the cell surface. (A) An internalization assay was performed on MJS HSV-1 gB (dark brown line), MJS BoHV-1 gB (pink line), or control MJSpuro (black line) cells stained on ice with anti-MHC class II L243 antibody and PE-conjugated IgG. The cells were then shifted to 37 °C for 20 or 40 min. The mean fluorescence intensities of remaining MHC II were assessed by flow cytometry for triplicate samples and compared with MHC II at time point 0 (set as 100%). The differences between MHC II levels were statistically insignificant. (B) For the MHC II export assay, the cells were stained on ice with a saturating amount of anti-MHC class II L243 antibody and incubated at 37 °C for 20 or 40 min in the presence of allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated L243 MAb detecting newly arrived MHC II. The mean fluorescence intensities of MHC II staining were normalized to the values for time point 0 samples and depicted as a percentage of the increase in MHC II appearance on MJSpuro (black line) or MJS-gB cells. Results are representative of three independent experiments. The statistical significance of differences between MHC II on MJSpuro and gB-expressing cells at 20 or 40 min was estimated by a t-test; p ≤ 0.01.