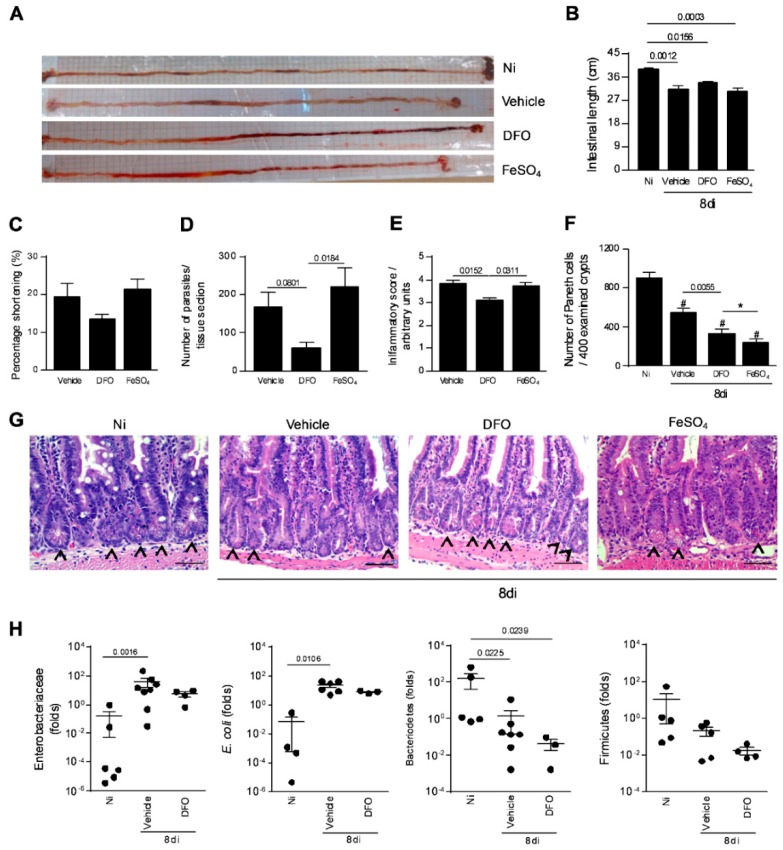
Figure 4.
Small intestine parasitism, inflammatory alterations, and relative quantification of some intestinal bacterial population in T. gondii-infected mice treated with an iron chelator or iron supplemented. Gross picture of the small intestine of non-infected (Ni) or infected C57BL/6 mice with 20 ME-49 T. gondii cysts by oral route and treated with vehicle (PBS) or 300 mg/Kg of deferoxamine (DFO) or 100 mg/Kg of iron sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4) by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection one day prior to infection, and for an additional seven days post-infection (A). Intestinal length (B) and shortening percentage of the small intestine (C). Tissue parasitism in the small intestine was detected by immunostaining and quantified by tissue section (D). Inflammatory score in the small intestine (E). Quantification of Paneth cells in 400 intestinal crypts (F,G). Arrows indicate Paneth cells. Relative quantification of intestinal Enterobacteriaceae, E. coli, Bacteriodetes, and Firmicutes by qPCR (H). Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Sidak’s post-test (E,F) and Kruskal Wallis followed by Dunn’s post-test (B, D, H). (*)(#) p < 0.0001; (#) differences in relation to non-infected (Ni) mice. Scale bar = 50 µm.