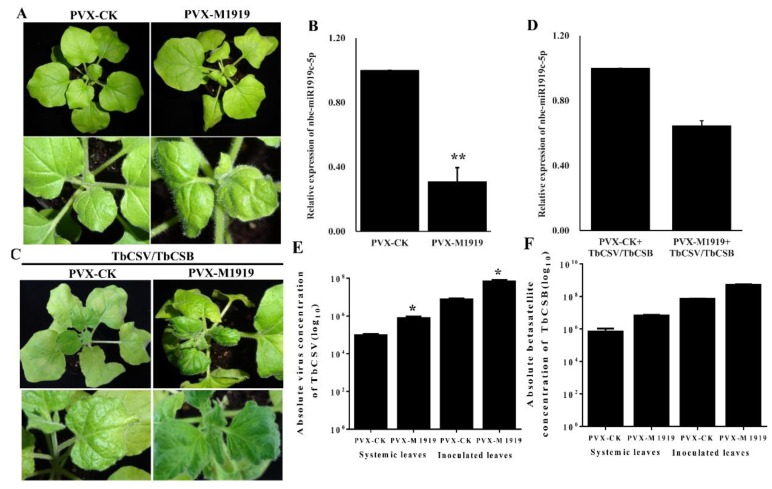
Figure 2.
Suppression of nbe-miR1919c-5p expression enhances the leaf curling symptom induced by TbCSV/TbCSB infection and viral DNA accumulation. (A) A potato virus x (PVX)-based miRNA vector (PVX-M1919) was used to suppress the expression of nbe-miR1919c-5p. At 7 dpi, the PVX-M1919-inoculated plant showed strong leaf curling symptoms but not the control plant (PVX-CK). (B) qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of nbe-miR1919c-5p in the PVX-M1919-inoculated plants was significantly reduced compared with the control plants. (C) The PVX+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated and the PVX-M1919+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants were photographed 7 days after the second inoculation. Only the PVX-M1919+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants showed severe leaf curling symptoms. (D) qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of nbe-miR1919c-5p in the PVX-M1919+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants was significantly reduced. (E) Detections of TbCSV DNA copy numbers in the inoculated and the systemic leaves harvested from the PVX+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants or the PVX-M1919+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants. (F) Detection of TbCSB DNA copy numbers in the inoculated and the systemic leaves harvested from the PVX+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants or the PVX-M1919+TbCSV/TbCSB-inoculated plants. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; determined by the Student’s t-test.