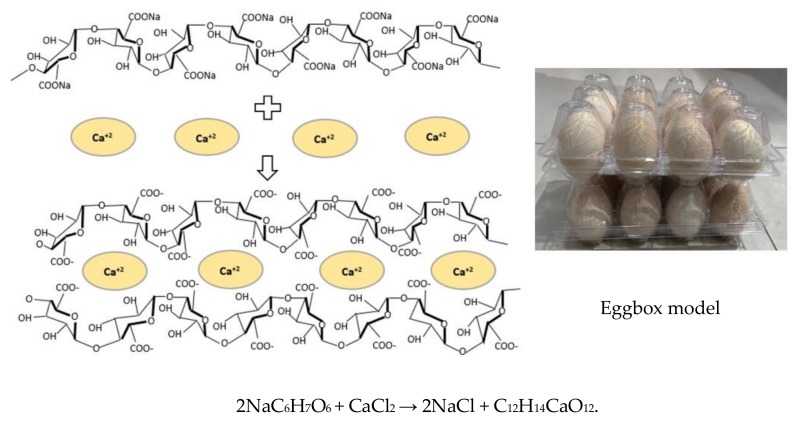
Figure 2.
The formation mechanism for calcium alginate. Sodium alginate (NaC6H7O6) reacts with calcium chloride (CaCl2) to generate calcium alginate (C12H14CaO12), which is a gelatinous material. The two chemicals are rearranged, so they bond (like the eggbox model) to form a gelatinous (jello-like) substance.