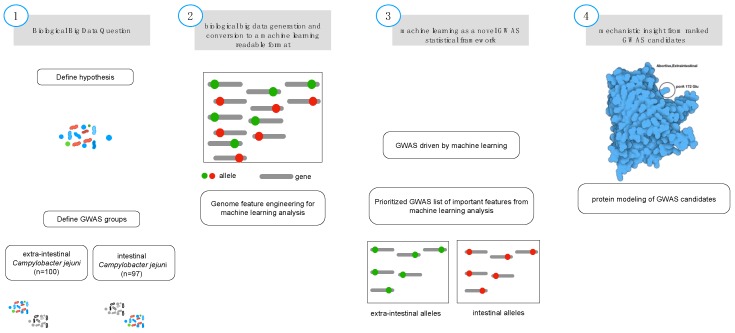
Figure 1.
Biological feature engineering of genomic data for machine learning analysis. A critical step in feature engineering is selection of the appropriate comparison groups to enable classification of alleles that are related to the specific phenotype of interest (i.e., intestinal (controls; diarrheal; n = 108) and extraintestinal (cases; abortive; n = 85) (Step 1). Population-wide allelic variants (red dot = intestinal, green dot = extraintestinal) that result from variant calling (Step 2) and are used as the input features for machine learning analysis (Step 3). The predicted model generated from the machine learning analysis is inspected for the most predictive features using biological context, input, and protein modeling (Step 4) that represents a non-synonymous mutation from the genomic population of allelic variants (n = 193).