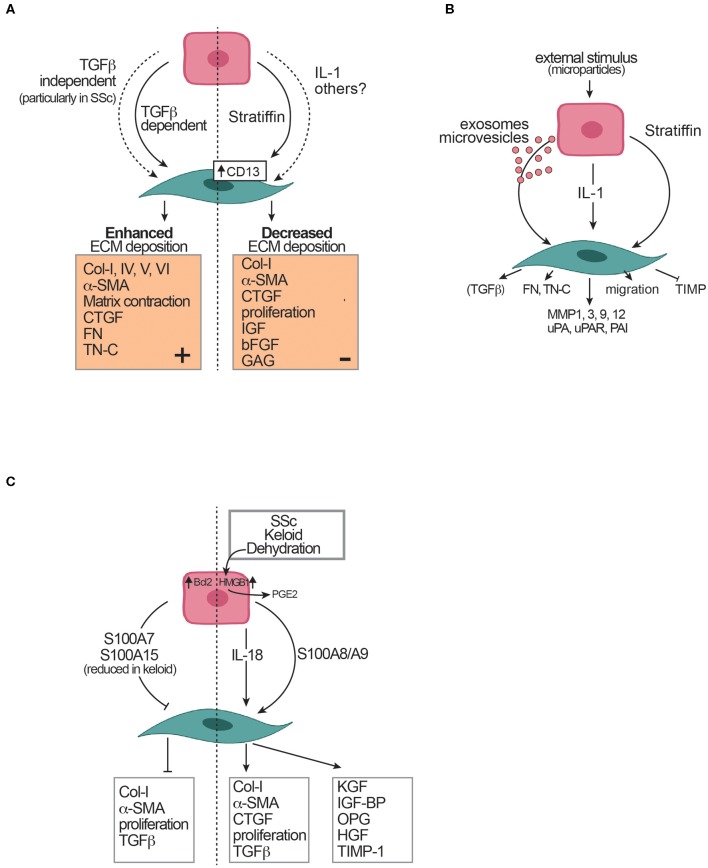
Figure 4.
Effects of keratinocytes on fibroblasts and extracellular matrix (ECM). (A) Controversial effects of keratinocytes on ECM deposition. (B) Mediators of keratinocyte effects on fibroblasts. (C) Skin pathological conditions and their effects on the crosstalk between keratinocytes and fibroblasts. The dotted vertical line separates controversial evidence. Arrowheads indicate enhancement. Blunted heads indicate inhibition. αSMA, alpha-smooth muscle actin; Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; Col, collagen; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; FN, fibronectin; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; HMGB1, high mobility group box-1; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IGF-BP, insulin-like growth factor binding protein; KGF, keratinocyte growth factor; MMP, metalloproteinase; OPG, osteoprotegerin; OSM, oncostatin M; PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; S100A7, psoriasin; S100A8/A9, calprotectin; S100A15,koebnerisin; SSc, Systemic sclerosis; SSc-F, SSc fibroblasts; SSc-K, SSc keratinocytes; TGF, Transforming growth factor; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of MMP; TN-C, tenascin C; TNFα, Tumor necrosis factor α; uPA, urokinase-type plasminogen activator; uPAR, urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.