FIGURE 3.
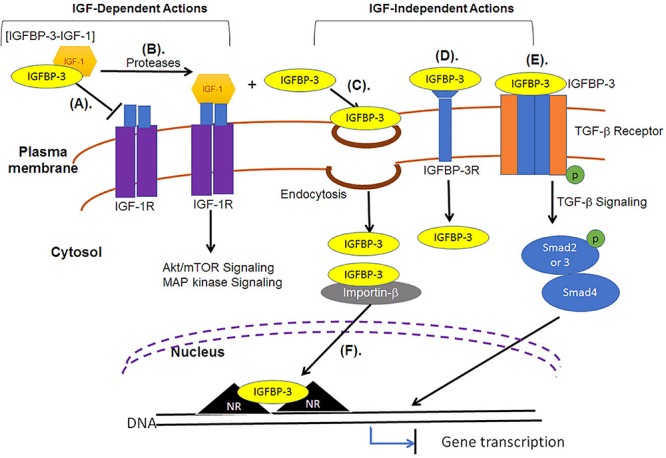
IGF-dependent and IGF-independent roles of IGFBP-3. (A) IGF-dependent roles of IGFBP-3 include the transport of IGFs in a binary complex, the state in which it cannot associate with IGF-1R. (B) Regulated proteolysis of the binary complex releases IGF, and free IGF can associate with the receptors (IGF-1R) to activate Akt/mTOR or MAP kinase signaling pathways. (C) IGFBP-3 can be internalized independent of IGFs into the cytosol through various endocytic mechanisms, including fluid-phase uptake, caveolae-mediated and clathrin-mediated endocytosis. (D) IGFBP-3 can associate with membrane proteins, including TGFβVR or IGFBP-3R and induce apoptosis. (E) IGFBP-3 can directly associate with TGF-β receptor to regulate the downstream Smad signaling. (F) IGFBP-3 can interact with importin-β through its nuclear localization signal (NLS) sequence and is transported into the nucleus, where IGFBP-3 can bind with nuclear receptors (NR) to inhibit gene transcription that can induce apoptosis.
