Fig. 2.
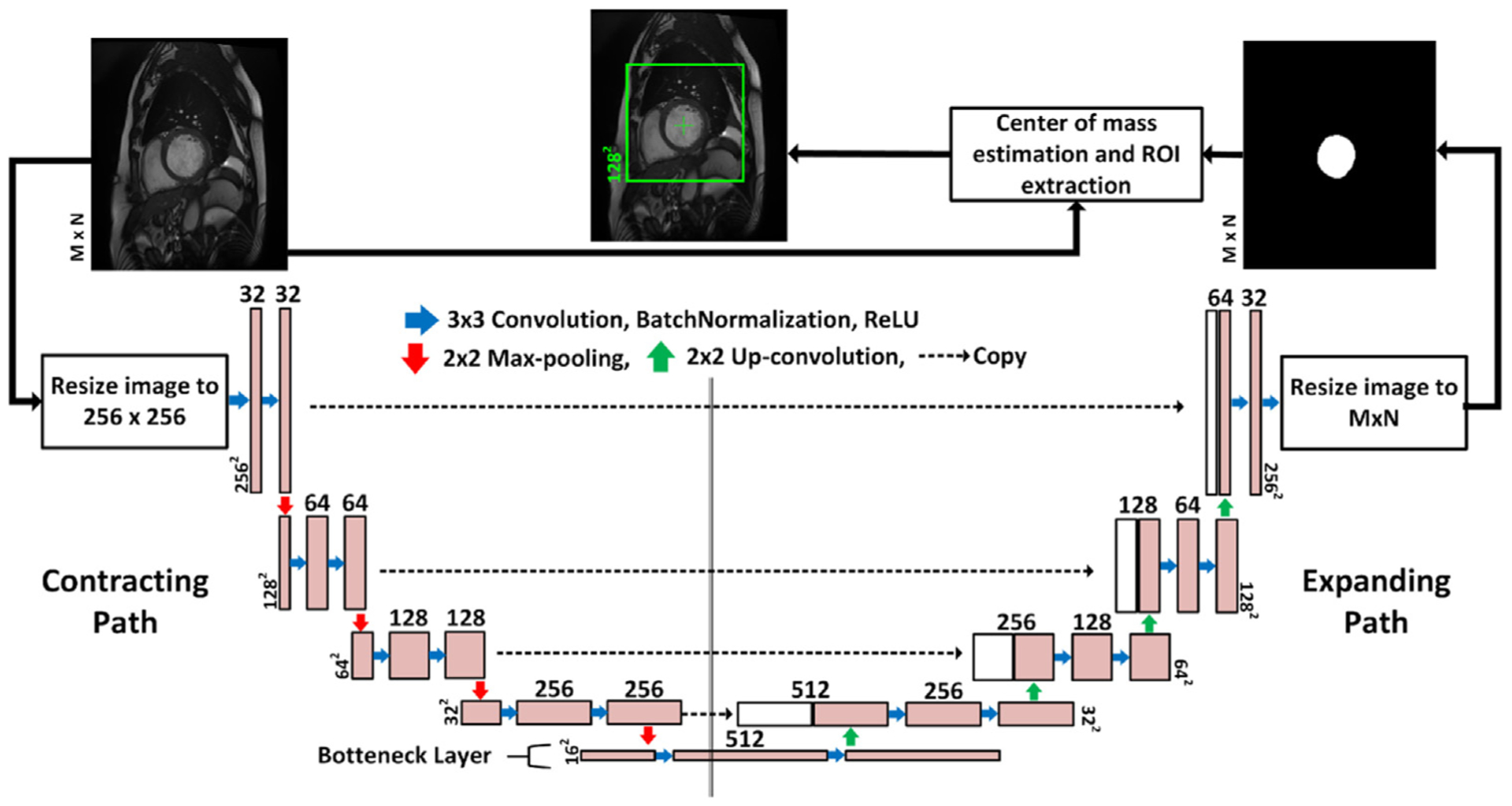
The LV-ROI extraction process using a fully convolutional network named FCN1. The input to the network is the original 2D CMR images which are re-sized to 256 × 256 pixels and the output is segmentation maps for the LV cavity, which are re-sized again to the same spatial dimension as the input. The blue arrow indicates convolution operation with a kernel size 3 × 3, and the number of kernels increases from 32 to 512 in the contracting path, and decreases from 512 to 1 in the expanding path. Zero-padding was used to maintain the same spatial resolution after convolution. The red (green) arrow refers to max-pooling (up-convolution) operation that decreases (increases) the spatial dimension by a factor of 2. Finally, the dashed arrow copies contextual information from the contracting path and concatenates it to the expanding path.
