Figure 5.
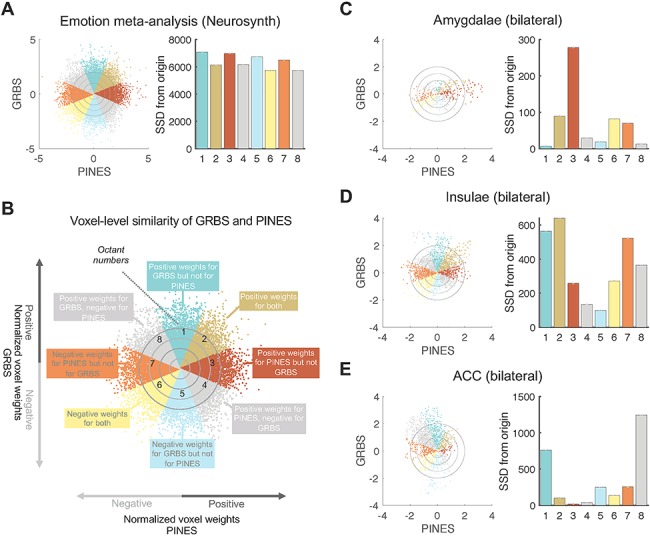
Voxel-level spatial similarity between GRBS and picture-induced negative emotion signature (PINES). (A) Scatter plots displays normalized voxel (within the Emotion mask) beta weights for GRBS (y-axis) and PINES (x-axis). Bars on the right represent the sum of squared distances from the origin (0,0) for each octant. This value integrates the number of voxels and their combined weights in each octant, we compute. (B) Differently colored octants indicate voxels of shared positive or shared negative (Octants 2 and 6, respectively), selectively positive weights for GRBS (Octant 1) and for PINES (Octant 3), selectively negative weights for GRBS (Octant 5) and for PINES (Octant 7), and voxels where the voxel weights of the two signatures went in opposite directions (Octants 4 and 8). (C) Voxel-level spatial similarity in bilateral amygdalae shows positive weights for PINES, but not for GRBS, as reflected by the high SSDO in Octant 3. (D) Voxel-level spatial similarity in bilateral insulae shows strongest weights in the Octants 1, 2, and 7, indicating many positive weights for guilt specifically (Octant 1), as well as shared positive weights across the two signatures (Octant 2), but also some many voxels with negative weights in the PINES (Octants 6–8). (E) Voxel-level spatial similarity in ACC shows almost exclusively positive weights for GRBS, which were mostly near-zero or even negative for PINES (Octants 1 and 8).
