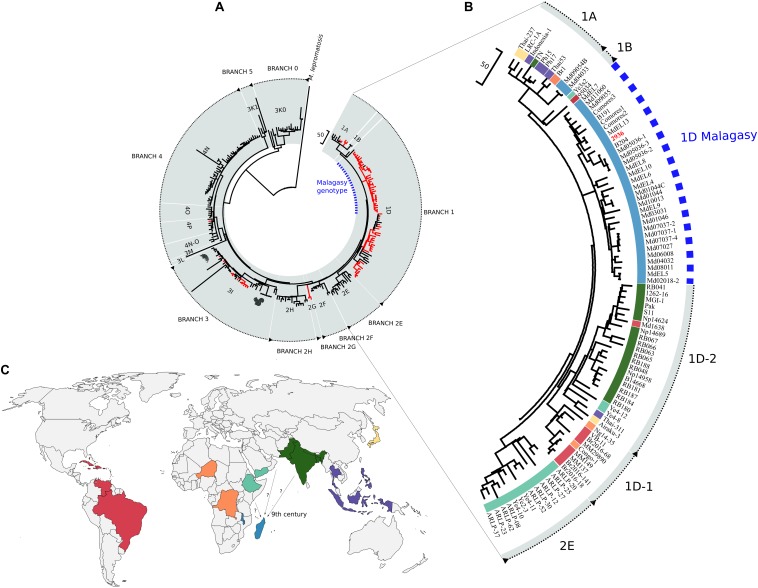
FIGURE 2.
Phylogeography of Mycobacterium leprae strains. (A) Maximum parsimony tree of 241 genomes of M. leprae representing the nine branches and the 16 genotypes. Support values were obtained by bootstrapping 500 replicates. Branch lengths are proportional to nucleotide substitutions. The tree is rooted using Mycobacterium lepromatosis. The 1D-Malagasy genotype, discovered in this investigation, is shown in blue. Newly sequenced genomes are shown in red. (B) Zoom into branch 1 (genotypes 1A, 1B, 1D, and the 1D-Malagasy) and 2E of the maximum parsimony tree from (A). The 1D-Malagasy genotype is indicated with the dotted blue line and the strain from Malawi in bold red. (C) Global distribution of the genotypes from the branches 1 and 2E. Genotypes are colored as in (B). Strains from the canonical 1D are found in 12 countries, while the 1D-Malagasy is found only in Madagascar, the Comoros, and Malawi. The arrows indicate possible routes of leprosy introduction into Madagascar and Comoros with the estimated time frame.