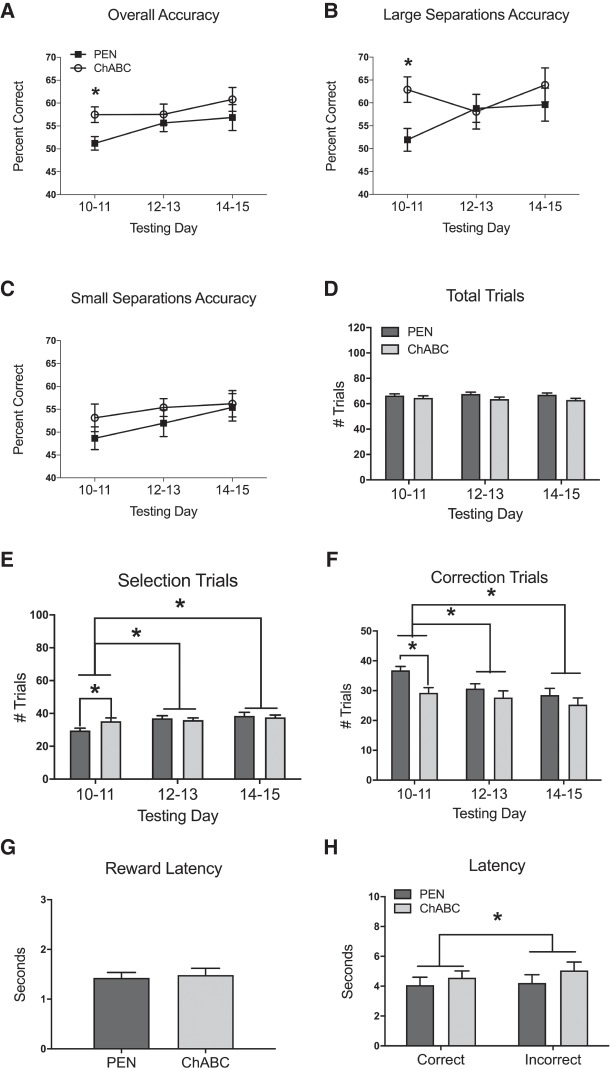
Figure 3.
Effects of PEN or ChABC infusions into the mPFC on TUNL with a 20 sec delay period (Condition 4). All values represent the mean ± SEM of the testing days. (A) ChABC-treated rats had a significantly higher overall percent accuracy than PEN-treated rats over the first 2 d of testing, but not over the full 6 d of testing. (B) ChABC-treated rats had a significantly higher percent accuracy on trials with large stimulus separations compared to PEN-treated rats over the first 2 d of testing, but not over the full 6 d of testing. ChABC had no effect on percent accuracy in trials with small stimulus separations (C) or the number of total trials completed (D). (E) ChABC-treated rats completed significantly more selection trials than PEN-treated rats over the first 2 d of testing, but not over the full 6 d of testing. Rats performed significantly more selection trials on testing days 12–13 and 14–15 compared to testing days 10–11. (F) ChABC-treated rats completed significantly fewer correction trials than PEN-treated rats over the first 2 d of testing, but not over the full 6 d of testing. Rats performed significantly fewer correction trials on testing days 12–13 and 14–15 compared to testing days 10–11. ChABC had no effect on reward latency (G), correct latency (H), or incorrect latency (H). Incorrect choice latency was significantly longer than correct choice latency (H). PEN, n = 12; ChABC, n = 11. Note that accuracy of 50% is chance performance in the TUNL task. (*) P < 0.05. Note that accuracy of 50% is chance performance in the TUNL task.