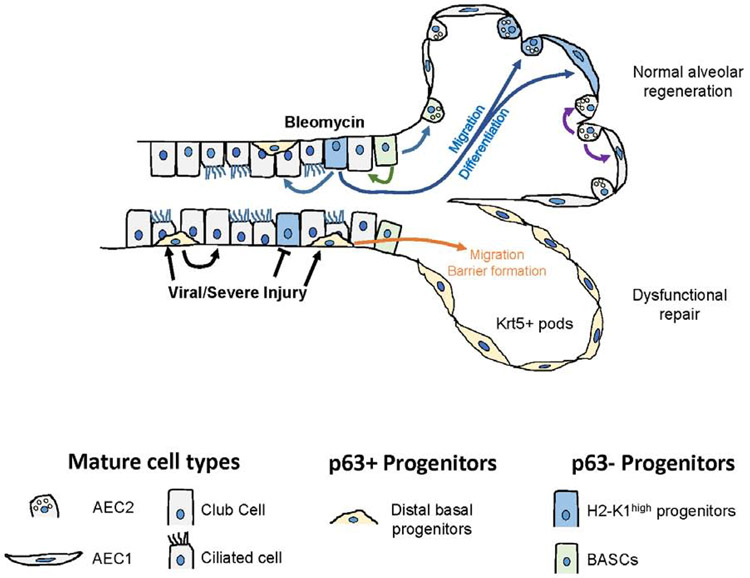
Figure 7: Injury-specific mobilization of distal airway stem/progenitor cells.
Distinct airway progenitors activate and expand depending on the type of injury. Newly identified H2-K1high progenitors are transcriptionally highly similar to mature club cells but have unique regenerative characteristics that are identified through single cell mRNA-seq. These cells are preferentially targeted during viral injury, which leaves p63+ distal basal cells as the primary effectors of alveolar injury resolution. In bleomycin injury, p63neg H2-K1high progenitors, along with BASCs, are mobilized to promote regeneration of normal alveolar epithelium.
See also Figure S7.