Figure A.2.
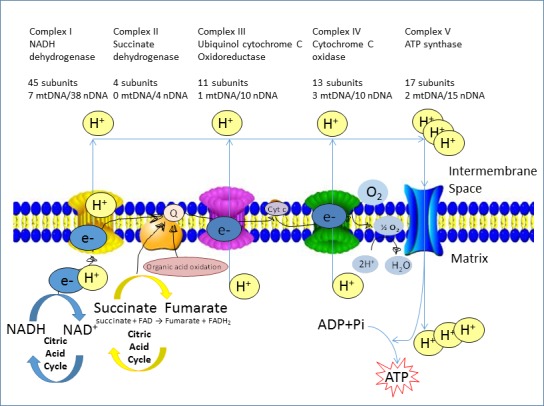
The electron transport chain in the mitochondrion. CI (NADH‐coenzyme Q reductase or NADH dehydrogenase) accepts electrons from NADH and serves as the link between glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation and the electron transport chain. Complex II also known as succinate‐coenzyme Q reductase or succinate dehydrogenase, includes succinate dehydrogenase and serves as a direct link between the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. The coenzyme Q reductase or Complex III transfers the electrons from CoQH2 to reduce cytochrome c, which is the substrate for Complex IV (cytochrome c reductase). Complex IV transfers the electrons from cytochrome c to reduce molecular oxygen into water. Finally, this gradient is used by the ATP synthase complex (Complex V) to make ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; nDNA: nuclear DNA
