Figure 2. E3 ligases RHA3A/B interact with and monoubiquitinate BIK1.
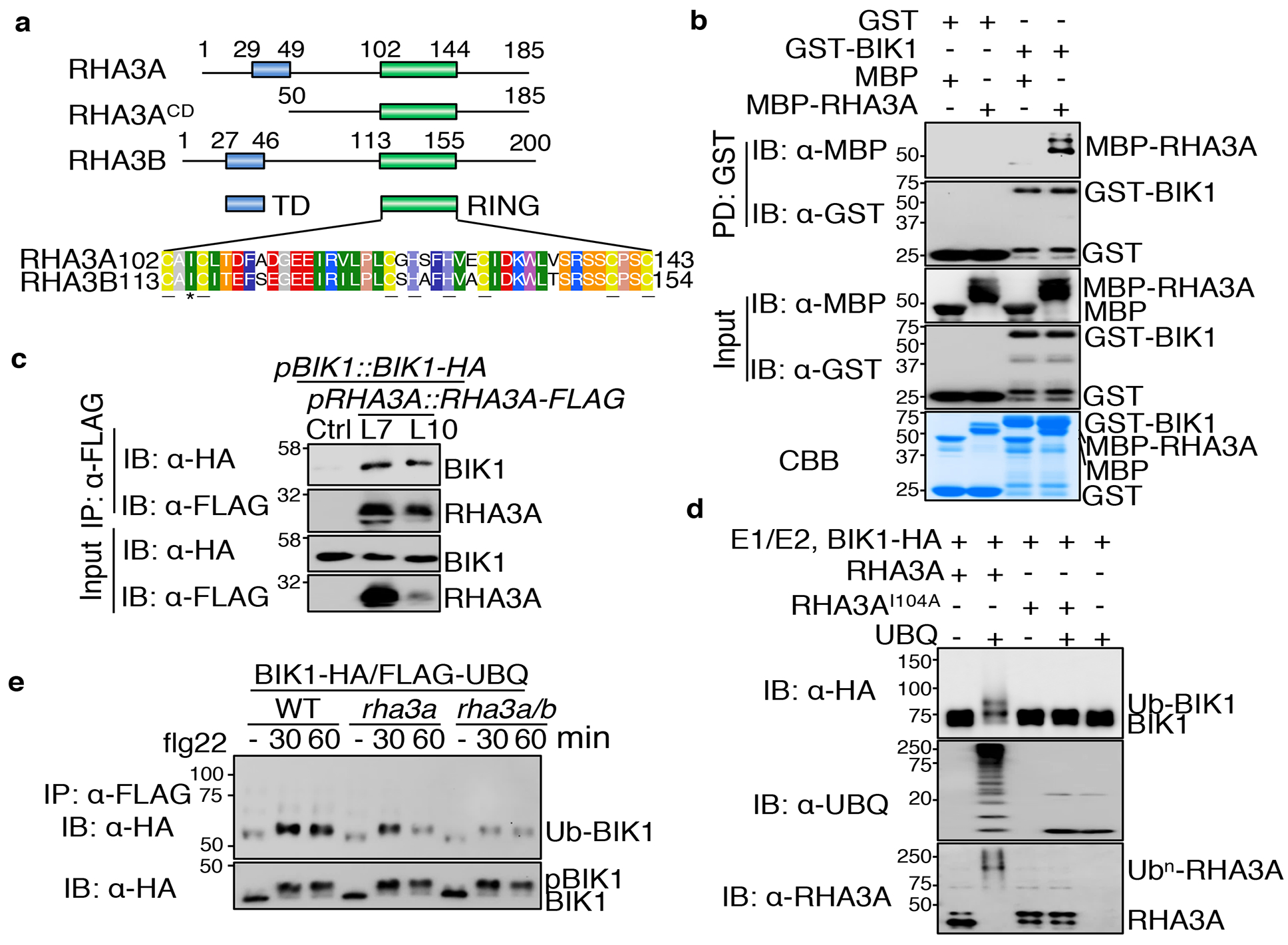
a. Domain organization of RHA3A/B. TD: transmembrane domain; RING: E3 catalytic domain; RHA3ACD: cytoplasmic domain. Amino acid positions and the sequence of RING domain are shown. Cysteine (C) and histidine (H) residues which coordinate zinc are underlined. Isoleucine (I) involved in E2-RING interaction is labeled with *. b. BIK1 interacts with RHA3A. GST or GST-BIK1 proteins immobilized on glutathione sepharose beads were incubated with MBP or MBP-RHA3ACD-HA proteins. Washed beads were subjected to IB with α-MBP or α-GST (top two panels). Input proteins are shown by IB (middle two panels) and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining (bottom). c. BIK1 associates with RHA3A. Transgenic plants carrying pBIK1::BIK1-HA and pRHA3A::RHA3A-FLAG (Line 7 and 10) were used for Co-IP assay with α-FLAG agarose and immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with α-HA or α-FLAG (top two panels). Bottom two panels show BIK1-HA and RHA3A-FLAG expression. d. RHA3A ubiquitinates BIK1. GST-RHA3ACD or its I104A mutant was used in the ubiquitination reaction containing GST-BIK1-HA, E1, E2, and ATP. e. RHA3A/B are required for BIK1 ubiquitination. The rha3a/b and rha3a plants were used for protoplast isolation followed by transfection of BIK1-HA and FLAG-UBQ. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
