Figure 3. Identification of RHA3A-mediated BIK1 ubiquitination sites.
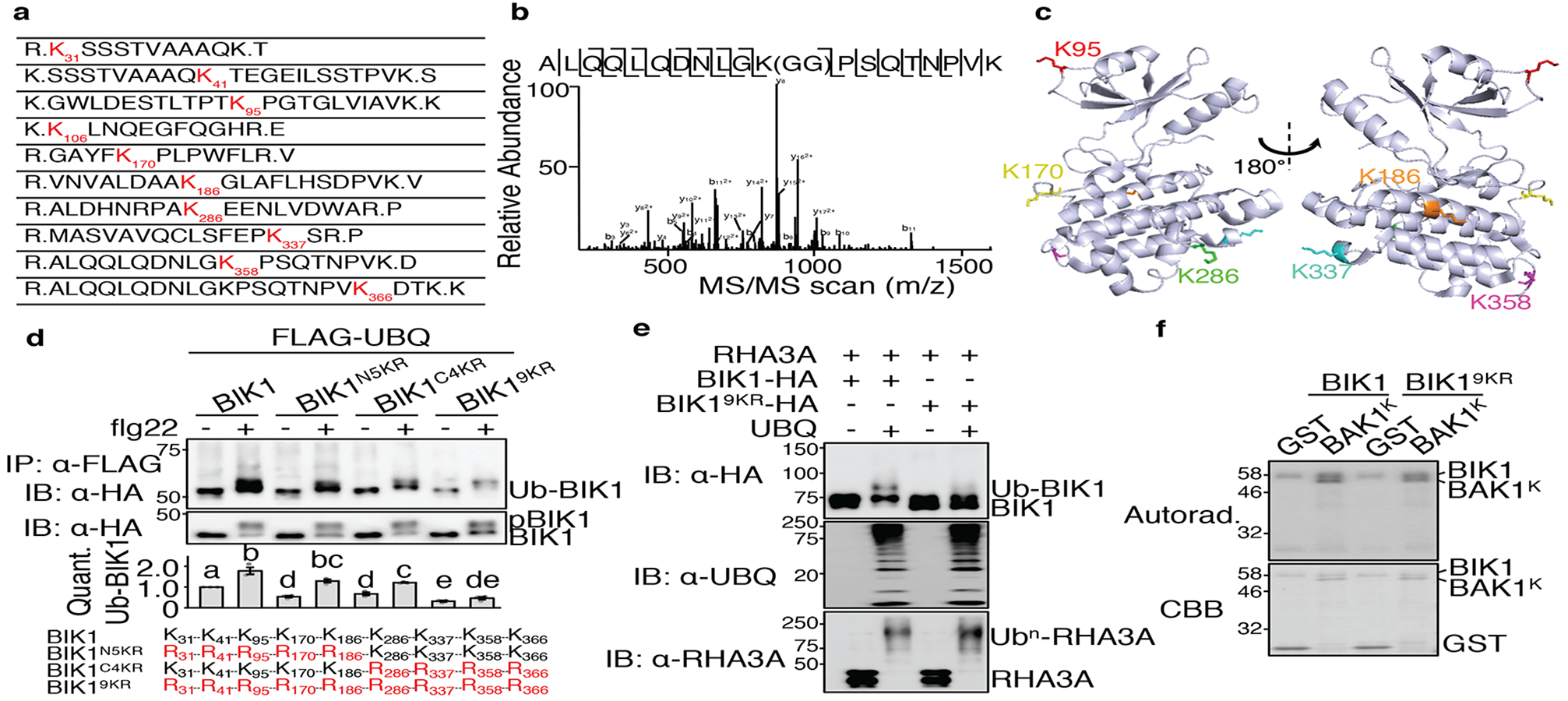
a. BIK1 is ubiquitinated by RHA3A at multiple lysine residues. Ubiquitinated lysine residues with a diglycine remnant by LC-MS/MS analysis are marked as red with amino acid positions. b. MS/MS spectrum of the peptide containing K358 is shown. c. Structure of BIK1 labeled with six lysine identified as ubiquitination sites. Structural information was obtained from protein data bank (PDB ID: 5TOS) and analyzed by PyMOL. d. BIK19KR is compromised in flg22-induced ubiquitination. FLAG-UBQ and HA-tagged BIK1 mutants were expressed in protoplasts followed by 100 nM flg22 for 30 min. Quantification of BIK1 ubiquitination fold change is shown as overlay of dot plot and means ± SEM (middle). Different letters indicate significant difference with others (P<0.05, One-way ANOVA, n=3). Mutated lysine for BIK1 mutants are in red (bottom). e. RHA3A is unable to ubiquitinate BIK19KR. The assay was performed as in Fig. 2d. f. BIK19KR exhibits normal in vitro kinase activity. The kinase assay was performed using GST-BIK1 or GST-BIK19KR as the kinase and GST or GST-BAK1K (kinase domain) as the substrate. The experiments except MS analyses were repeated three times with similar results.
