Extended Data Figure 4. RHA3A/B interacts with BIK1 in vivo.
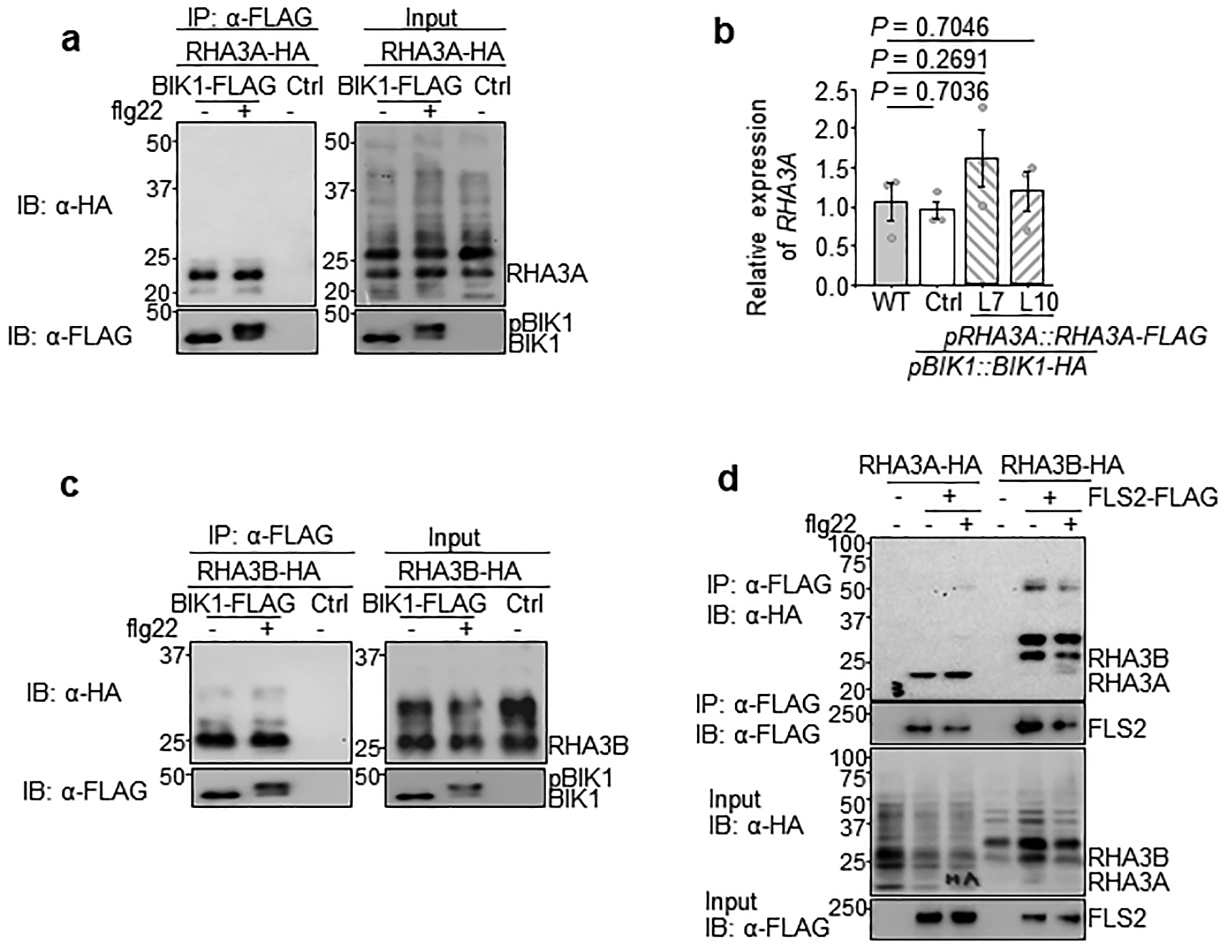
a. BIK1 interacts with RHA3A in a Co-IP assay. RHA3A-HA was co-expressed with BIK1-FLAG or Ctrl in protoplasts followed by 100 nM flg22 treatment for 15 min. The Co-IP assay was carried out with α-FLAG agarose and immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with α-HA or α-FLAG antibody (left). The right panels show BIK1-FLAG and RHA3A-HA proteins. b. RHA3A expression in pRHA3A::RHA3A-FLAG/pBIK1::BIK1-HA transgenic plants. qRT-PCR was carried out to detect RHA3A transcripts using ACTIN2 as a control. The relative gene expression from WT (set as 1), pBIK1::BIK1-HA (Ctrl) and two independent transgenic lines (line 7 and 10) is shown. Data are shown as means ± SEM (One-way ANOVA, n=3). c. BIK1 associates with RHA3B independent of flg22 treatment. RHA3B-HA was co-expressed with BIK1-FLAG or Ctrl in protoplasts followed by 100 nM flg22 treatment for 15 min. Co-IP assay was carried out with α-FLAG agarose and immunoprecipitated proteins were immunoblotted with α-HA or α-FLAG antibody (left). Right panels show BIK1-FLAG and RHA3B-HA proteins before IP. d. FLS2 interacts with RHA3A and RHA3B in a Co-IP assay. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results.
